Protection and Switchgear Interview Questions and Answers:
Following are the below Protection and Switchgear Interview Questions and Answers, Protection and Switchgear Important Questions and Answers
1. Mention the essential features of the power system protection.
Ans.
- Speed and Time,
- Selectivity,
- Sensitivity,
- Stability,
- Simplicty and Economics,
- Reliability.
2. Explain the need for overlapping the zones of protection.
Ans.
- The circuit breakers are located in the connections to each power system element.
- This provision makes it possible to disconnect only the faulty element from the system.
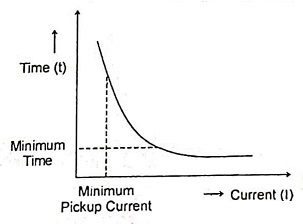
3. Classify the different types of overcurrent relays based on the inverse time characteristics.
Ans.
- Static Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay,
- Directional Static Overcurrent Relay,
- Inverse Time Overcurrent Relay.
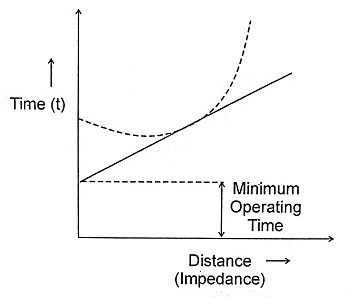
4. Derive and draw the characteristics of impedance relay.
Ans. Operating time α z α distance
Time of operation of relay α V/I z α distance.
Where
- V = Voltage in Volts,
- I = Current in Amps.
- Z = Impedance in Ohms.
5. Explain the basic difference between the measurement and protection CT’s.
Ans.
- Measuring current transformers – used in conjunction with ammeter, wattmeter etc.
- Protection current transformers – used in association with relays, trip coils, pilot wires etc.
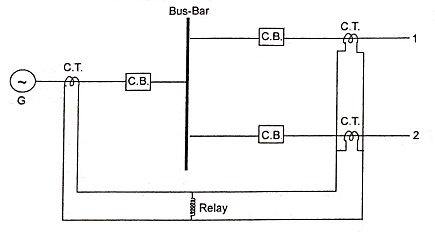
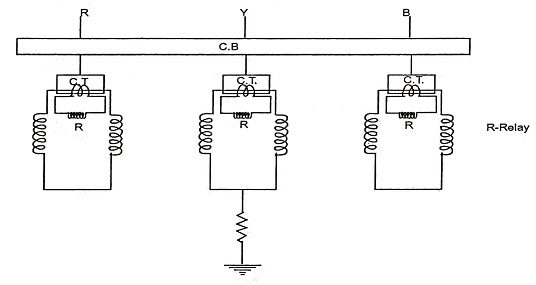
6. Draw the protection scheme for busbar protection.
Ans. G → Generator, C.T. → Current Transformer C.B. → Circuit Breaker
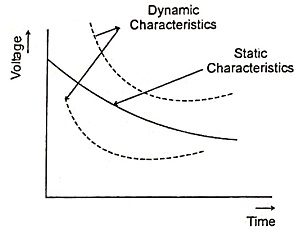
7. Explain the static and dynamic arc characteristics.
Ans.
When a graph of instantaneous values of votlage between the electrodes values of current then it gives arc characteristics. If current changes rapidly with time, the characteristics are known as dynamic characteristics. While if current changes slowly or if the rate of change of current is small then the characteristic are static.
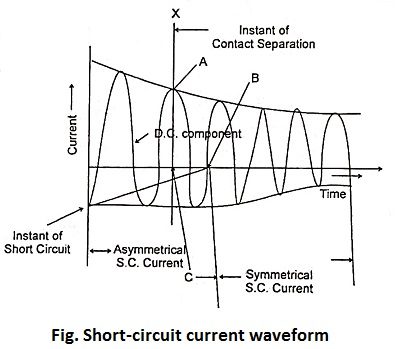
The short circuit current contains a dc components, which dies out gradually.
In the beginning, the short circuit current is asymmetrical due to the dc component.
8. What is the need for multiple breakers in circuit breaking?
Ans. When the higher voltage operation to need small rating or multiple breakers is reudced arc in the contacts.
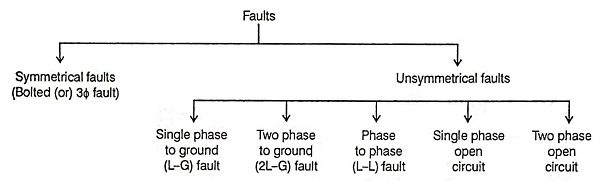
9. List out the types of faults in power system.
Ans. There are the following types of fourth in power system. They are,
- Symmetrical faults
- Unsymmetrical faults
- Single phase to ground (L – G) fault
- Two phase to ground (2L – G) fault
- Phase to phase (L – L) fault
- Open circuited phases
- Winding faults.
- Simultaneous faults.
10. Mention different types of overcurrent relay.
Ans.
- Definite-time overcurrent relay
- Instantaneous overcurrent relay
- Inverse-time overcurrent relay
- Inverse definite minimum time overcurrent relay
- Very inverse-time overcurrent relay
- Extremely inverse-time overcurrent relay.
11. What are the advantages of static relays over electroniagnetic relays?
Ans.
- Low burden on C.Ts and P.Ts
- Static relay consume less power
- Fast response and long life
- Less maintenance due to absence of morning parts
- Compact in size and greater sensitivity.
12. Draw a protection scheme to detect a turn-turn fault in a winding of an alternator.
Ans.
13. Why are current transformers required in protection schemes?
Ans.
- Current transformers are used to reduce the heavy current flowing in an element of a power system to low values.
- Besides reducing the current level, the C.T. also isolates the relay circuit from the primary circuit which is a high voltage power circuit and allows the use of standardized current rating for relays.
14. What are the different methods of high resistance arc interruption?
Ans.
- Lengthening the arc,
- Splitting of arc,
- Cooling of arc.
15. What are the problems encountered in DC circuit breaking?
Ans. The arc becomes unstable and the difference in voltage is supplied by inductance L. For decreasing values of current this voltage is negative and it tries to maintain the arc.
16. How does circuit breaker differ from a switch?
Ans. Circuit breaker is designed that it can be operated manually under normal conditions and automatically under fault conditions whereas switch will not operate under faulty conditions.
17. What are the chief requirements of the contact material for vacuum circuit breaker?
Ans.
- Contacts are required to be travelled by small distance.
- Contacts must be of less weight such that many repeated operations can be performed with this type.
18. What are the causes of faults in power system?
Ans.
- Internal causes of the equipment.
- Heavy short circuit current may causes damage to damage equipment or other element of the system due to over heating and high mechanical forces set up due to heavy current.
- Deterioration of Insulation.
19. Define zone of protection.
Ans. A protective zone covers one or at the most two elements of a power system. The protective zone covers are planned in such a way that the entire power system is collectively covered by them is known as zone of protections.
20. Mention any two applications of differential relay.
Ans.
- It can be differentiate the heavy load conditions and minor load conditions.
- Fault current can be easily identify the relay.
- Protection of generator and generator transformer unit protection of large motors and bus bars.
21. What are the features of directional relay?
Ans. A Directibnal power relay which operates when the power in the circuit flows in a particular direction. Thus it requires to sense the system voltage as well as the system current.
22. Give the limitations of Merz Price protection.
Ans. Since neutral earthing resistances are often used to protect circuit from earth fault currents, it becomes impossible to protect the whole of a star connected alternator. If an earth-fault occurs near the neutral point, the voltage may be insufficient to operate the relay. Also it is extremely difficult to find two identical CT’s. In addition to this there always an inherent phase difference between the primary and the secondary quantities and a possibility of current through the relay even when there is no fault.
23. Why bus bar protection is needed?
Ans.
- Fault level at busbar is high.
- The stability of the system is affected by the faults in the bus zone.
- A fault in the busbar causes interruption of supply to a large portion of the system Network.
24. What is RRRV?
Ans. It is the rate of rise of restriking voltage, expressed in volts per microsecond. It is closely associated with natural frequency of oscillation.
25. What do you mean by current chopping?
Ans. When interrupting low inductive currents such as magnetizing currents of the transformers shunt reactor, the rapid deionization of the contact space and blast effect may cause the current to be interrupted before the natural current zero. This phenomenon of interruption of the current before its natural zero is called current chopping.
26. What is dielectric test of a circuit breaker?
Ans. Dielectric test is used for schering bridge to identify the continuation faults, internal insulation failure, improve the power factor and loss of angle detection and dielectric losses.
27. What is surge absorber? How do they differ from surge diverter?
Ans. Surge Absorber: It is a protective device which reduces the steepness of wave front of a surge by absorbing surge energy.
Surge Absorber – It eliminates the surge, by absorbing the surge energy.
Surge Diverter – It eliminates the surge, by diverting the surge to earth.
28. Define the term “Insulation Coordination”.
Ans. As per IEEE 1313.1 the insulation co-ordination is “the selection of insulation strength consistent with expected overvoltages to obtain an acceptable risk of failure.”
29. Explain the secondary of current transformer should not be open.
Ans. Secondary of CT should not be open:
If the secondary of CT is left open, due to infinite impedance the current through secondary becomes zero and hence ampere turns produced by secondary which oppose primary ampere turns becomes zero. Since there is no counter mmf unopposed primary mmf produce high flux in core. This causes excessive core loss, and heavy induced emfs on primary and secondary side. This damages the insulation of winding. So the secondary of CT should not be kept open.
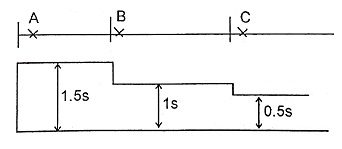
30. What is meant by time-graded system protection?
Ans. Time-Graded System of Protection:
It uses definite-time overcurrent relays. When a definite time relay operates for a fault current, it starts a timing unit which trips the circuit breaker after a preset time, which is independent of fault current. The operating time of relays is adjusted in increasing order from far end of feeder.
31. List the factors affecting the transient recovery voltage.
Ans. Factors Affecting Transient Recovery Voltage:
- Power factor.
- Circuit conditions.
- Armature reaction.
32. Give the advantage of SF6 circuit breaker over Air blast circuit breaker.
Ans. Advantages of SF6 Circuit Braker:
- Arcing time is very small due to the arc quenching propert of SF6.
- It is compact in size and silent in operation.
- Current chopping is minimised.
33. What are the basic requirements of circuit breaker?
Ans. Basic Requirements of Circuit Breaker:
- It requires a medium (Air, Oil, SF6 Gas) to quench the arc.
- It should have the ability to disconnect the faulty element in the power system.
- It should possess very high rupturing capacity.
- It should requires high speed reclosure.
- It should requires smaller space and very easy access to the contacts.
34. What are the various types of faults occurring in a power system?
Ans.
35. How is ‘arcing ground’ avoided?
Ans. Arcing ground can be avoided by earthing the system neutral solidly or through a resistance or reactance.
36. What is meant by directional relay?
Ans. It is able to detect whether the point of fault lies in the forward or reverse direction with respect to the relay location. It is able to sense the direction of power flow.
37. Why is under frequency relay required in a power system?
Ans. This relay will operates when the system frequency falls below a certain preset value of frequency. So it senses the lower system frequency.
38. What are the problems associated with bus zone differential protection?
Ans. There may be a false operation in case of an external fault. This is due to saturation of one of C.T. of faulted feeder. When the C.T. saturates, the output is reduced and the sum of all the C.T. secondary currents will not be zero.
39. What are the main safety devices available with transformers?
Ans.
- Overcurrent relays
- Percentage differential protection fuses
- Harmonic restraint relay
- Buchholz relay
- Earthfault relay
40. What is the principle involved in High Resistance Interruption?
Ans. The arc resistance is increased so as to reduce the current to a value insufficient to maintain the arc. When the current is interrupted the energy associated with its magnetic field appears in the form of electrostatic energy. A high voltage appears across the contacts of circuit breaker. If this voltage is more than the withstanding capacity of gap between the contacts, the arc will strike again.
41. Define the term “rate of rise of recovery voltage”.
Ans. It is defined as the slope of the steepest tangent to the restriking voltage curve. It is expressed in kV/µs.
42. Mention different types of circuit breakers.
Ans.
- Air blast circuit breakers
- Oil circuit breakers
- Vacuum circuit breakers
- SF6 (Sulphur Hexafluoride) circuit breakers.
43. What are the types of tests carried out on circuit breaker?
Ans.
Type test:
- Mechanical test
- Thermal test
- Dielectric (Insulation) test
- Short-circuit test
Routine test:
- Milli-volt drop test
- Operational test
44. Write the effects of power system faults.
Ans. The power system faults may cause an interruption of supply to consumers:
- Heavy short circuit current may damage the equipment.
- Arcs associated with short circuits may cause fire hazards.
45. Enumerate the significance of back protection.
Ans.
- If primary relay fails to operate, then the back-up protective relay will clear the fault.
- Back-up relay operates after a time delay to give the primary relay sufficient time to operate.
46. Write the effects of arc resistance.
Ans.
- Arc resistance will affect the performance of different types of distance relays.
- Arc resistance causes under reach in MHO relay.
- Due to arc resistance, the impedance relay will fail to operate.
47. List out the applications of static relays.
Ans.
- Static relay is used to achieve many varied and complex distance protection characteristics.
- It is used for differential protection schemes.
48. Write the function of earth fault relay.
Ans.
- Used for protection of an element of power system against earth faults.
- Earth fault relays are more sensitive.
49. What is meant by relay operating time?
Ans. Relay operating time means the time which elapses between the instant when the actuating quantity exceeds the pick-up value to the instant when the relay contacts close.
50. List out the various methods of arc interruption.
Ans.
- High Resistance Interruption.
- Current Zero Interruption.
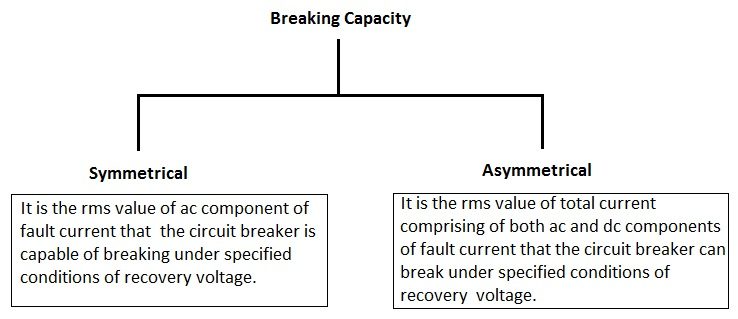
51. Enumerate the breaking capacity of circuit breaker.
Ans.
52. What is the role of protection relay in a modern power system?
Ans.
- To disconnect faulty part quickly.
- To improve or enhance the transient stability of power system.
- To give command to the circuit breaker to isolate the faulty element of the system depending on abnormality occured in electric circuit.
53. What is meant by pick-up current?
Ans. It is the minimum current in the relay coil at which the relay starts to operate. When the relay coil current is equal to or greater than the pick up value, the relay energise the trip coil which opens the circuit breaker.
54. What are the necessary conditions for two alternating fluxes acting on a common rotor (a) to produce some torque, (b) to produce maximum torque.
Ans.
- To produce some torque, two alternating fluxes should have a phase shift.
- To produce maximum torque, two alternating fluxes are shifted in phase by 90°.
55. What is meant by differential relay?
Ans. A differential relay is one that operates when the phasor difference of two or more similar electrical quantities exceeds a predetermined value.
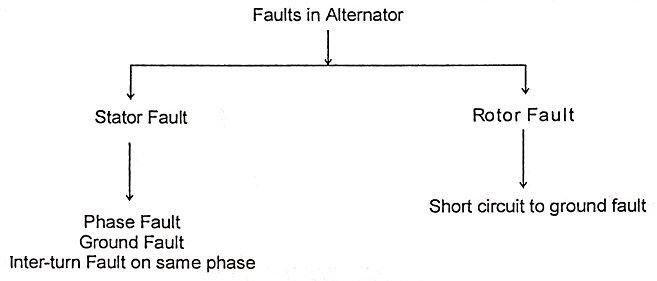
56. Discuss the different faults that may occur in an alternator.
Ans.
57. W hat is the importance of bus-bar protection?
Ans. Bus-bar protection is important because:
- If a fault develops in busbar, considerable damage and disruption of supply will occur.
- Bus-bar forms a vital part of supply system.
- System voltage and short-circuit capacities will buildup if busbars are left unprotected.
58. Discuss the arc phenomenon in a circuit breaker.
Ans. When a short-current occurs, a heavy current flows through the contacts of circuit breaker before they are opened by protective system. At the instant when the contacts begin to separate, the temperature and heat produced in the medium between contacts to ionise air or vapourise oil. Ionised air acts as conductor and an arc is struck between the contact the potential difference between the contacts is small and is just sufficient to maintain the arc.
59. What is meant by recovery voltage?
Ans. It is the normal frequency (50 Hz) r.m.s. voltage that appears across the contacts of circuit breaker after final arc extinction.
60. State the advantages of SF6 circuit breaker.
Ans.
- There are no carbon deposits so that insulation problems are eliminated.
- It has very short arcing time.
- It can interrupt much larger currents.
61. Write the sources of fault power.
Ans. The sources of fault power originate in all the generating and other connected plants which undernormal conditions take power from the system.
- A drop in frequency or voltage under short-circuit conditions is common and in this event, synchronous machines will feedback into the system for a short period. Similarly, large induction motors where considerable flywheel effet is available act as generators in the event of reduced frequency.
62. List out the duties of fault limiting reactors.
Ans.
- To reduce the short circuit currents so that circuit breakers with lower short circuit breaking capacity can be utilized.
- To limit inrush current when starting a large motor.
63. What are the types of fuses?
Ans.
(i) Rewirable type fuse
- Semi-enclosed type fuse
- Open type fuse.
(ii) Catridge or Totally enclosed type fuse
- High Rupturing Capacity (HRC) catridge fuse
- D-type catridge fuse.
64. What are the different types of zones of protection?
Ans.
- Generator protective zone
- Bus bar protective zone
- Transformer protective zone
- HV switchgear protective zone
- Primary and Back up protection.
65. Write the inference of resistance switching.
Ans.
- To reduce circuit severity by controlling R.R.R.V
- To suppress overvoltages due to current chopping in air blast circuit breaker.
66. What is meant by autoreclosing?
Ans. The automatic reclosure of a circuit-breaker after a predetermined time following a fault tripping. Reclosing after predetermined time, when line to ground fault takes place is known as single-phase autoreclosing. During three phase autoreclosing all the three phases, which are independent of the types of fault are opened after predetermined time.
67. Write the function of isolating switch.
Ans.
- To open circuit during no-load,
- To close a circuit if a negligible current is switched,
- To withstand normal system voltage.
68. Write the ratings of the circuit breaker.
Ans.
- Rated voltage in kV,
- Rated symmetrical breaking capacity in kA,
- Rated making capacity in kA,
- Rated short circuit current in kA,
- Rated frequency in Hz,
- Rated asymmetrical breaking capacity in kA.