Regulated and Switching Power Supplies Articles:
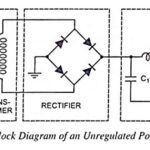
Regulated and Unregulated Power Supply: Almost all electronic devices used in electronic circuits need a dc source of power to operate. The source of dc power is used to establish the dc operating points (Q-points) for the passive and active electronic … (Read More)
Characteristics of Regulated Power Supply: The quality of power supply depends on different factors such as its load voltage, load current, voltage regulation, source regulation, output impedance, ripple rejection etc. Some of the characteristics of regulated power supply are discussed below. 1. … (Read More)
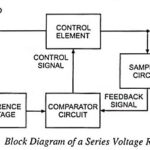
Series Voltage Regulator – Block Diagram and Working Principle: The basic connection of a series voltage regulator circuit is shown in the block diagram given in Fig. 43.4. The series element controls the magnitude of the input voltage that gets to the … (Read More)
Transistor Series Voltage Regulator or Emitter Follower Voltage Regulator: A simple series voltage regulator using an NPN transistor and a zener diode is shown in Fig. 43.5. This circuit is called a series regulator because collector and emitter terminals of the … (Read More)
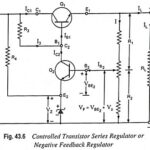
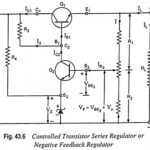
Controlled Transistor Series Regulator or Negative Feedback Regulator: A controlled transistor series regulator is shown in Fig. 43.6. This Controlled Transistor Series Regulator circuit is quite similar to that of a simple transistor series voltage regulator except that an additional transistor … (Read More)
Controlled Transistor Series Regulator with Short Circuit Protection: Controlled Transistor Series Regulator with Short Circuit Protection – If the load resistance RL is reduced or load terminals are shorted accidentally, a very large load current will flow in the circuit shown … (Read More)
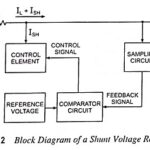
Shunt Voltage Regulator Block Diagram: A shunt voltage regulator provides regulation by shunting current away from the load. The block diagram of such a voltage regulator is depicted in Fig. 43.12. The input unregulated voltage provides current to the load. Some … (Read More)
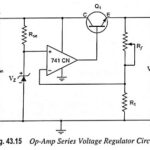
Op Amp Regulators: The Op Amp Regulators which includes Op-Amp Series Voltage Regulator Circuit, Current Limiting circuit, Foldback Limiting and Op-Amp Shunt Voltage Regulator Circuit. Let us see one by one in detail. Op-Amp Series Voltage Regulator Circuit: Op-amp series voltage regulator circuit … (Read More)
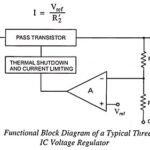
IC Voltage Regulators: IC voltage regulators are versatile and relatively inexpensive and are available with features such as a programmable output, current-voltage boosting, internal short-circuit current limiting, thermal shutdown, and floating operation for high voltage applications. IC Voltage regulators comprise a class … (Read More)
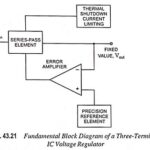
Three Terminal IC Voltage Regulators – Block Diagram: The latest generation of IC voltage regulators has devices with only three pins: one for the unregulated input voltage, one for the regulated output voltage, and one for ground. The new devices can … (Read More)
Fixed Positive Voltage Regulators: The series 7800 regulators provide eight voltage options, ranging from 5 to 24 V, as indicated in Table 43.2. These ICs are designed as fixed voltage regulators and with adequate heat sinking. Although these devices do not … (Read More)
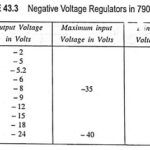
Fixed Negative Voltage Regulator: As we have seen many times previously, positive and negative regulated power supply voltages are often required. In response, many manufacturers have developed negative three-terminal regulators. They offer the same types of features and protection as are … (Read More)
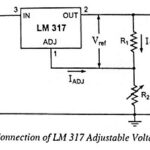
Adjustable Voltage Regulators: Sometimes variable voltage is required and under such a situation adjustable voltage regulators is used. A number of IC regulators, like LM317, LM338, and LM350, are adjustable regulators. They have maximum load currents from 0.10 to 1.5 A. For … (Read More)
LM340 Series Voltage Regulator: This LM340 Series Voltage Regulator is typical of the three-terminal voltage regulators. The block diagram is shown in Fig. 43.27. The built-in reference voltage Vref drives the noninverting input of an op-amp. The operational amplifier consists of … (Read More)
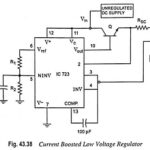
What is Current Limiting Protection? The circuit arrangement for IC 723 as low voltage or high voltage regulator has no protection. If short circuiting takes place (when load demands more current), regulator IC makes efforts to provide it at a constant … (Read More)
What is Current Foldback? The current limiting technique maintains a constant load current at some specified value and under overload condition, the Vout drops to zero. But, in case of short circuiting under overload conditions the maximum current flows into the … (Read More)
What is Current Boosting in Voltage Regulator? Current Boosting in Voltage Regulator – IC723 regulator is limited to provide a maximum current of 140 mA. To increase its current capacity, we add a transistor Q by connecting its collector to pin … (Read More)
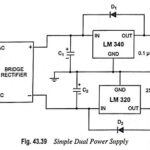
What is Dual Power Supply? -Circuit Diagram and its Workings: Many discrete and ICs need bipolar (dual power supply or ± V) supplies. This can be easily accomplished with two three-terminal regulators, as illustrated in Fig. 43.39. Opposite-phase ac is provided … (Read More)
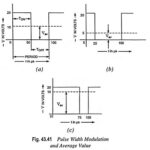
Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) or Switching Regulators: Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) – The regulated power supplies described earlier were basically linear voltage regulators. A linear voltage regulator possesses many limitations: The input transformer is bulky and is a very expensive … (Read More)
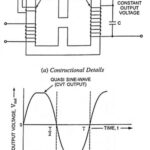
Constant Voltage Transformer (CVT) – Construction and Working Principle: With the popularization of PCs, the constant voltage transformers (CVTs) have also become equally popular. The Constant Voltage Transformer is simply a magnetic transformer of a special construction that has a capacitor … (Read More)
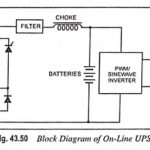
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) – Block Diagram and its Workings: Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) – Most of us take the mains ac supply for granted and use it almost casually without giving the slightest thought to its inherent shortcomings and the … (Read More)