Resonators and Waveguides Articles:
Rectangular Waveguides: As we know already that the term skin effect indicated that the majority of the current flow (at very high frequencies) will occur mostly along the surface of the conductor and very little at the center. … (Read More)
Reflection of Electromagnetic Waves by a Conducting Surface: In view of the way in which signals propagate in waveguides, it is now necessary to consider what happens to Reflection of Electromagnetic Waves when they encounter a conducting surface. An electromagnetic plane … (Read More)
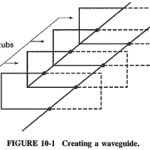
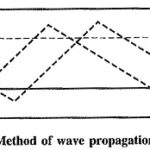
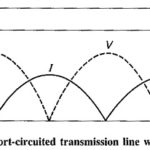
Parallel Plane Waveguide: As we know already in connection with transmission lines, that reflections and standing waves are produced if a line is terminated in a short circuit, and that there is a voltage zero and a … (Read More)
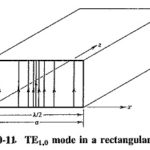
Rectangular Waveguide Derivation: When the top and bottom walls are added to our parallel-plane waveguide, the result is the standard Rectangular Waveguide Derivation used in practice. The two new walls do not really affect any of the results so far obtained … (Read More)
Circular Waveguide: It should be noted from the outset that in general terms the behavior of waves in circular waveguide is the same as in rectangular guides. Analysis of behavior: The laws governing the propagation of waves in waveguides are independent of the … (Read More)
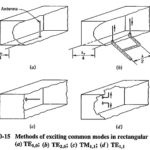
Methods of Exciting Waveguides: In order to launch a particular mode in a Methods of Exciting Waveguides, some arrangement or combination of one of more antennas is generally used. However, it is also possible to couple a coaxial line directly to … (Read More)
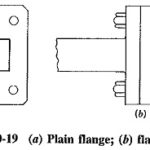
Waveguide Coupling: When waveguide pieces or components are joined together, the Waveguide Coupling is generally by means of some sort of flange. The function of such a flange is to ensure a smooth mechanical junction and suitable electrical characteristics, particularly low … (Read More)
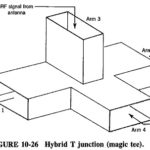
Waveguide Junctions: When it is required to combine two or more signals (or split a signal into two or more parts) in a waveguide system, some form of multiple junction must be used. For simpler interconnections T-shaped junctions are used, whereas … (Read More)
Impedance Matching and Tuning in Waveguide: We know that suitably chosen series or parallel pieces of transmission line had properties which made them useful for providing resistive or reactive impedances. It is the purpose of this section to show how the … (Read More)
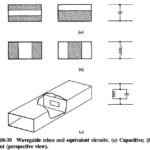
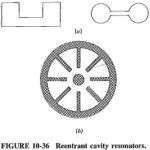
Cavity Resonators: A cavity resonators is a piece of waveguide closed off at both ends with metallic planes. Where propagation in the longitudinal direction took place in the waveguide, standing waves exist in the resonator, and oscillations can take place if … (Read More)
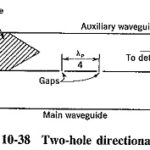
Directional Coupler Waveguide: We already know that a transmission-line Directional Coupler Waveguide. Its applications were indicated at the time as being unidirectional power flow measurement, SWR measurement and unidirectional wave radiation. Exactly the same considerations apply to waveguides. Several directional couplers for … (Read More)
Waveguide Isolator and Circulators: It often happens at microwave frequencies that coupling must be strictly a one-way affair. This applies for most microwave generators, whose output amplitude and frequency could be affected by changes in load impedance. Some means must be … (Read More)
Waveguide Mixers and Detectors: As we know that ordinary transistor and tube RF amplifiers eventually fail at microwave frequencies, because of greatly increased noise, compared with their low-frequency performance. Unless a receiver is to be very low-noise and extremely sensitive (in … (Read More)
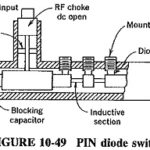
Waveguide Switch Design: It is often necessary to prevent microwave power from following a particular path, or to force it to follow another path; as at lower frequencies, the component used for this purpose is called a switch. Waveguide Switch Design … (Read More)