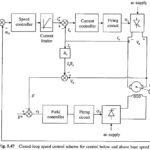
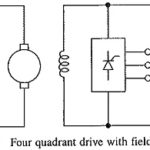
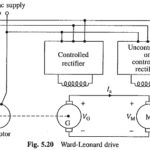
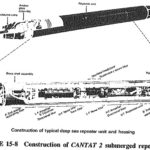
Variable Speed Constant Frequency Generator
Variable Speed Constant Frequency Generator: Variable Speed Constant Frequency Generator (VSCF) involves generation of electrical power at fixed frequency and fixed voltage from a variable speed prime mover coupled to…