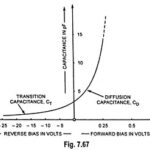
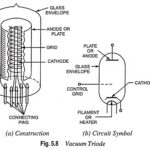
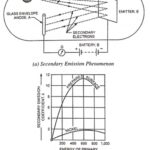
Transition and Diffusion Capacitance
Transition and Diffusion Capacitance: Transition and Diffusion Capacitance - Electronic devices are inherently sensitive to very high frequencies. Most shunt capacitive effects that can be ignored at lower frequencies due…