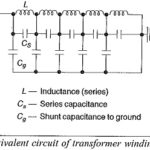
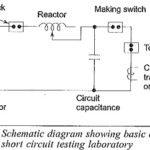
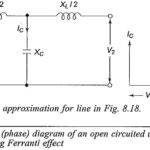
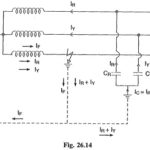
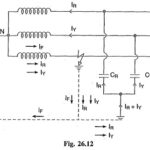
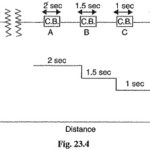
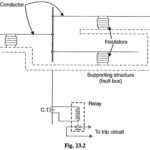
Protection of Alternators and Transformers Articles
Protection of Alternators and Transformers Articles: Protection of Alternators: The generating units, especially the larger ones, are relatively few in number and higher in individual cost than most other equipment’s.…