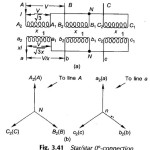
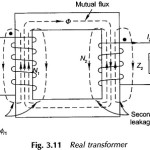
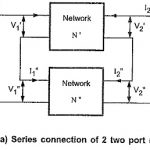
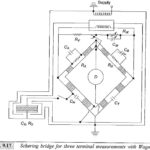
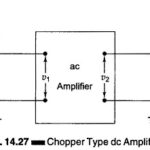
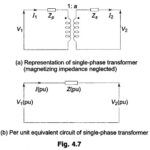
Three Phase Transformer Connections
Three Phase Transformer Connections: In generation, transformation, transmission and utilization of electric energy it can be shown that it is economical to use the three-phase system rather than the single-phase.…