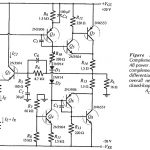
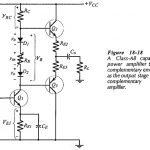
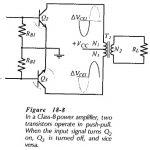
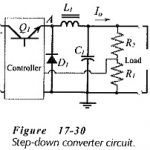
Linear and Switching Voltage Regulators Articles
Linear and Switching Voltage Regulators Articles: Transistor Series Voltage Regulator: When a low power zener diode is used in the simple Transistor Series Voltage Regulator, the load current is limited…