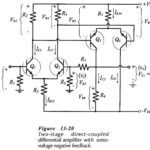
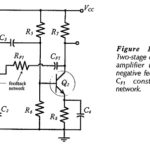
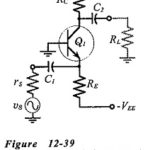
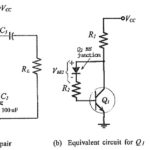
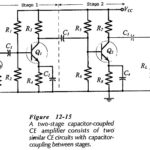
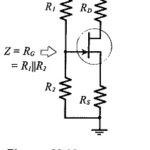
Two Stage Differential Amplifier with Negative Feedback
Two Stage Differential Amplifier with Negative Feedback: The circuit shown in Fig. 13-20 has a Two Stage Differential Amplifier with Negative Feedback with npn BJTs, and a direct-coupled pnp transistor…