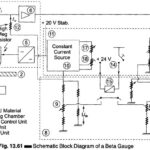
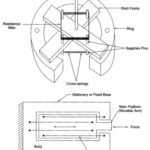
Measurements of Thickness using Beta Gauge
Measurements of Thickness using Beta Gauge: Beta Gauge - A common and characteristic feature of a radioactive element is that they disintegrate spontaneously to produce fresh radioactive elements called daughter…