Class A Push Pull Amplifier – Working Principle, Advantages & Disadvantages
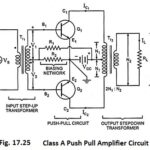
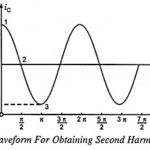
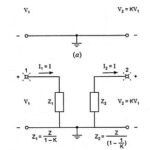
Class A Push Pull Amplifier - Working Principle, Advantages & Disadvantages: A Class A Push Pull Amplifier circuit is shown in Fig. 17.25. By Class A Push Pull Amplifier means…