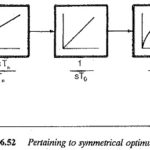
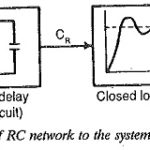
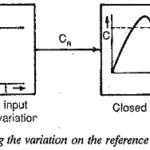
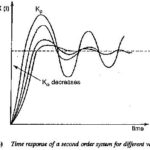
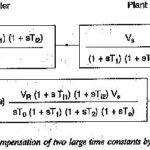
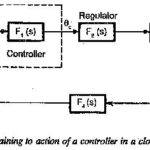
Symmetrical Optimum
Symmetrical Optimum: Symmetrical Optimum - Sometimes automatic control systems contain integrating also besides first order delay elements, proportional elements and deadzones. Such a system when compensated on the basis of magnitude…