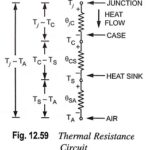
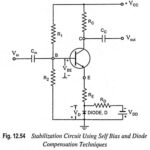
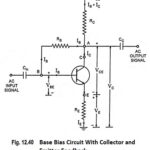
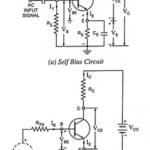
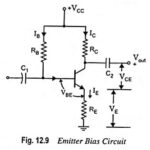
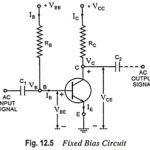
Advantages and Disadvantages of JFET
Advantages and Disadvantages of JFET: Junction field-effect transistors combine several merits of both conventional (or bipolar) transistors and vacuum tubes. Some of these advantages and disadvantages of JFET are enumerated…