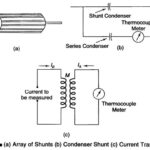
Measurements of very Large Currents by Thermocouples
Measurements of very Large Currents by Thermocouples: Measurements of very Large Currents by Thermocouples - Thermocouples instruments with heaters large enough to carry very large currents may have an excessive…