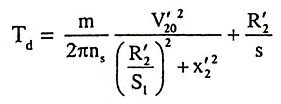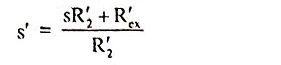Solid State Drives Interview Questions and Answers:
Following are the below Solid State Drives Interview Questions and Answers, Solid State Drives Important Questions and Answers
1. State the requirements of an adjustable speed drive.
Ans.
a) Stable operation: The speed-torque characteristics such that stable operation of the drive is assured in all the four quadrants over a wide range of speeds.
b) The drive motor should also have a good transient response. The drive should return to its original operatirig condition very quickly in case of disturbance. If there is a step change in torque or speed the drive must attain its new operating point quickly without any large over shoots. It must operate with stability, not have a sluggish transient respone not be very oscillatory and have a suitably chosen damping.
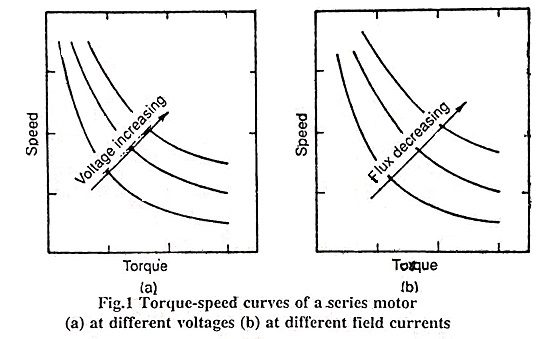
2. Draw the torque-speed curves of a series motor a varying flux and various voltages.
Ans.
3. What are the uses of phase controlled rectifiers in DC drives?
Ans. Since SCR is used in phase controlled rectifier for the armature. The output voltage could be varied (depending on phase delayed control) from the rectifier and hence the voltage to the motor.
4. What is discontinuous conduction mode?
Ans. In a dual converter one converter operates as rectifier and the other operates as inverter. In the discontinuous conduction mode only one converter operates at a time and carries the load current. The firing pulses applied to the thyristors of the two converters are scheduled so that only one of them operates at one time. In this mode the response is slow due to discontinuous current operation. This mode has lower losses and higher efficiency than continuous conduction mode.
5. What is the reactive power due to harmonics in single phase AC voltage controller fed drive?
Ans. The reactive power required by a converter is due to the phase control and as well as commutation. Unlike the active power, which is decided by the fundamental only, the control reactive power is decided by the harmonics also. The reactive power required because of phase control is VdiIdsinα and it increases with firing angle.
6. What are the influences of the type of load on a ac motor drive?
Ans. The loads are two types those which provide active torque and those which provide passive torque. Active torque are due to gravitational force. The active torque continue in the same direction even after the direction of motion is reversed. Passive torques are due to friction or due to shear. Passive torques always oppose motion even if the direction of drive changes.
7. State the limitation of rotor resistance control.
Ans.
- The speed control range is limited by the resistance.
- The method is very inefficient because of losses in the resistance.
8. Mention few general features of an induction motor on a CSI.
Ans.
- The power and control circuits are complicated when comparecl to square wave inverter.
- Both single and multimotor operation is possible.
- The parallel operation of many inverters on the same bus system is possible.
- Open loop operation is possible. The inverter has a fast response and a very good dynamic behaviour.
9. Give two salient features of cycloconverters used to control the synchronous motor speed.
Ans.
- Absence of gears reduces the cost and maintenance.
- The cycloconverter is ideally suitable for such a low frequency supply.
10. What happens to the stator current of a synchronous motor when V/f is kept constant?
Ans. The armature current is independent of frequency when the effects of resistance have been corrected particularly at low frequencies Which leads to straight forward and simple control of stator current to maintain constant flux with motor. This makes the operation of a synchronous motor for current source inverter possible.
11. Classify the mechanical loads based on their speed-torque characteristics.
Ans.
- Constant and continuous loads paper making machines and centrifugal pumps and fans operate for a long item under the same conditions.
- Continuous variable loads. Hoister inches conveyors, metal cutting, paths.
- Pulsating loads generally machines with crank shaft are categorized in this type of loads such as textile forms reciprocating pumps, compressors frame saws.
- Impact loads machine used with drives and having heavy flywheels as for example rolling mills, presses, shearing machines, forging hammers.
- Short-time intermittent loads. Hoisting mechanisms, excavators, roller trains, Cranes.
- Short time loads servo motors used for remote control of damping rods for drilling machines.
12. What are the disadvantages of using a motor of wrong rating?
Ans. A motor chosen should neither be too small nor too big to drive a particular load. In the former case it may not be able to drive the load satisfactorily and may get unduly overloaded with a temperature rise much greater than permissible value. Sometimes it may run the risk of damage or even burn out. In the latter case the drive motor is not fully loaded operates with poor efficiency and involves capital investment.
13. Mention two advantages of a dual converter fed DC drive when compared to conventional Ward-Leonard scheme.
Ans. In dual converter dc drive both speed control and regeneration are possible.
14. Why thyristors are not preferred now a days for chopper fed DC drives?
Ans. Generally transistor choppers are preferred over thyristor because they can be operated at a much higher frequency (2.5 to 10 KHz) whereas thyristor can be operated upto (1 KHz).
15. What happens to the performance of AC motor if the stator voltage control technique is adopted with frequency being constant?
Ans. Introducing an ac voltage controller provides a variable voltage across the load at the same frequency as the source.
16. Constant torque loads are not suitable for AC voltage controller fed inductor motor drive. Why?
Ans. Constant torques are not suitable for ac voltage controller fed induction motor drive because of increased loss and heating.
17. List the demerits of the rotor resistance control using SCR switching with external resistance.
Ans.
- The speed control range is limited by resistance.
- This method is very inefficient because of loss in the resistance.
- It is suitable for intermittent loads such as elevators.
- At low speed the motor has very low efficiency.
- The rotor current in this case is non sinusoidal. The harmonics of rotor current produce torque pulsations.
18. Why the power factor of the slip power recovery scheme of speed control of induction motor is low?
Ans. Drive input power is the difference between motor input power and the power fed back. Reactive input power is the sum of motor and inverter reactive power. Therefore drive has a low power factor throughout the range of its operation.
19. What are the modes of speed control of a synchronous motor?
Ans. Variable frequency control may employ any of the two modes.
- True synchronous mode,
- Self controlled mode
20. What are the applications of cycloconverter fed synchronous motor drive?
Ans. It finds application in high power pump and blower type motor.
21. Classify the drive motors based on their speed torque characteristics.
Ans. A low spe.d hoist is an example of a load where the torque is constant and independent of speed-low speed hoist motor. There are drives where coulomb friction dominates over other torque components consequently the torque is independent of speed – e.g. paper mill drive, Fans, Compressors, Aeroplanes, Centrifugal pumps, Ship propellers, colturies high speed hoists are examples Where load torque is a function of speed. In fans, compressors aeroplanes the load torque is proportional to the square of the speed.
Traction is an example where the load torque also depends on the position or path followed.
22. List the factors that govern the choice of rating of a motor to be used as a drive element.
Ans. The rating of a motor to be used as a drive element depends upon the following factors.
- Heating effects of the motors.
- Environmental conditions.
- Loading conditions and classes of duty.
- Load inertia of inertias.
23. What is meant by critical speed in phase controlled dc drives?
Ans. Critical speed in phase controlled dc drives is the speed which separates continuous conduction and discontinuous conduction for a given firing angle and denoted ωmC.
24. What causes poor input power factor in phase controlled dc drives?
Ans. Phase controlled converter requires power for control and commutation. The harmonics do not contribute to the active power-loading but they contribute to the reactive loading of the line. Because of these the line power factor is poor.
25. What is the need for constant v/f ratio in variable voltage induction motor drives?
Ans. For the operation of motor at small steps it must be limited to the linear portion of the torque-speed curve. The torque developed is proportional to the square of air gap flux. Td α Φ2
To retain the maximum torque capability at all operating points the flux must be maintained at its rated value. To achieve this supply voltage must also be varied simultaneously with the frequency. One simple and approximate method is to vary the voltage proportional to frequency such that -v/f is constant.
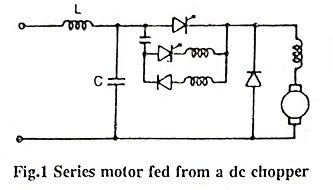
Give the expression for Torque of a static rotor resistance controlled three phase induction motor.
Ans.
where
where
- R′2 = Rotor resistance;
- R′ex = resistance included
27. Where are closed loop control schemes of induction motors preferred?
Ans. The closed loop control scheme of induction motor is preferred because
- Stabilization is readily obtained.
- Speed regulation on load may be reduced by means of a high gain speed control amplifier.
28. Name the different modes of operation of a synchronous motor derive.
Ans. The modes of operation of a synchronous drive.
- True synchronous mode,
- Self controlled mode.
29. What is meant by shunted motor connection of a DC series motor?
Ans. In this connection a part of the line current flows in the armature and field current is maintained at the line value by properly selection of the shunting resistance a desirable speed torque characteristic may be obtained. The higher field current stabilizes the speed of lower values and the smaller armature current develops a lower torque.
30. Why does a semiconverter offer a better input power factor than a full Converter?
Ans. Semiconverter operate at high power factor because semiconverter consumes less reactive power and have a less ripple in the motor current when compared with full converter.
31. Draw the diagram of a regenerative chopper fed separately excited D.C. motor drive.
Ans.
32. Name the methods of speed control applicable on the stator side of a three phase induction motor.
Ans. The following methods of speed control are available on the stator side of a three phase induction motor.
- Variable terminal voltage control.
- Variable frequency control driver stator voltage and frequency control.
33. When is an induction motor said to be working in the field weakening mode?
Ans. For speed control above base speed field control must be combined with armature voliage control. Speed control from zero to base speed should be done at the maximum field by armature voltage and control above base speed should be done by field weakening at the rated armature voltage.
34. What are the disadvantages of static rotor resistance control?
Ans. The main disadvantage of static rotor is the motor derating.
35. What is a Static Kramer drive?
Ans. The slip power recovery system for the speed control of slip ring induction motor is traditionally known as Kramer system.
36. What is a commutatorless dc motor?
Ans. A machine is to be self controlled if it gets its variable frequency from an inverters whose thyristors are fired in sequence using the information of rotor and stator voltages. The self controlled motor has the properties of a dc motor under steady state and dymanic conditions and is called commutator less motor. These machines have better stability behaviour. They do not fall out of step and do not have oscillatory behaviour as in normal synchronous motor.
37. How is the direction of rotation reversed in a brushless dc motor?
Ans. The direction of rotation in a brushless dc motor can be reversed by shifting the transistor base pulses by 180°.