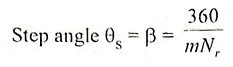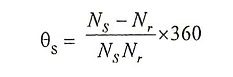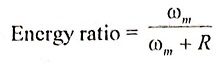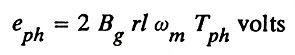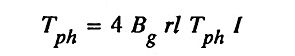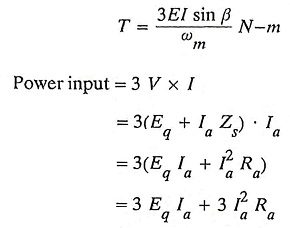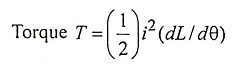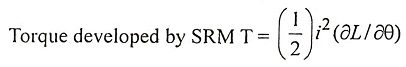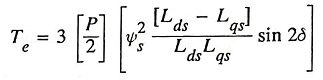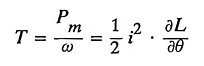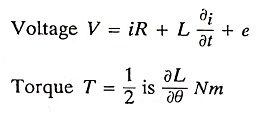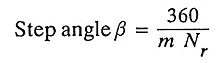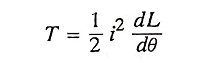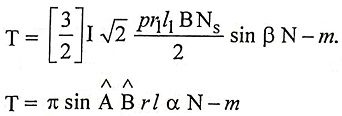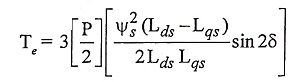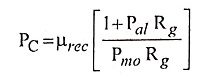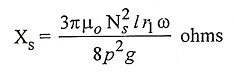Special Electrical Machines Interview Questions and Answers:
Following are the below Special Electrical Machines Interview Questions and Answers, Special Electrical Machines Important Questions and Answers
1. Write down the equation for step angle of stepper motor.
Ans.
where
- m = no. of phases
- Nr = no. of teeth on rotor
- Ns = no. of teeths/poles on stator
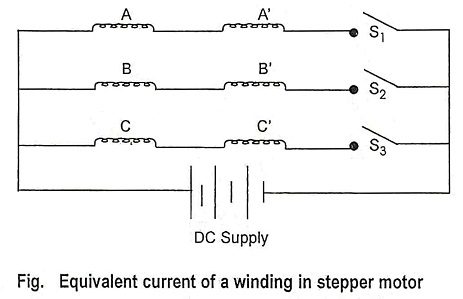
2. Draw the equivalent circuit of a winding in stepper motor.
Ans.
3. Define Energy Ratio.
Ans.
where ωm is the energy converted into mechanical ωm + R is the energy fed to the machine through power electronic circuitry from dc supply.
4. What is PMBLDC machine?
Ans. PMBLDC – Permanent Magnet Brushless DC machine, DC motors with solid state switches performing the function of commutation and that too brushless making these maintenance free motors are known as PMBLDC.
5. What is Electronic Commutation?
Ans. Power electronic switching devices used in commutator with the utilisation of position sensor are known as electronic commutation.
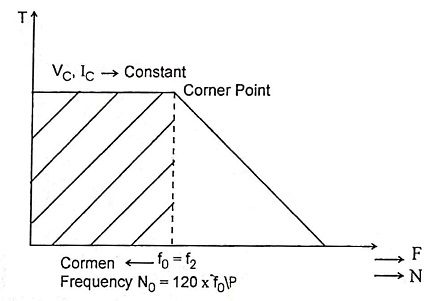
6. Draw the torque – speed characteristics of PMSM.
Ans.
7. Define synchronous reluctance.
Ans. The stator has a 3Φ symmetrical winding, which creates sinusoidal rotating magnetic field in the air gap and reluctance torque is developed because the induced magnetic field in the rotor has a tendency to cause the rotor to align with the stator field at a minimum reluctance position and stator rotates at synchronous speed.
8. List the types of synchronous reluctance motors.
Ans.
Based on the construction of the rotor type, synchronous reluctance motor is classified as
- Salient rotor (segmental type).
- Radially laminated Rotor (flux barrier type).
- Axially laminated rotor type.
9. List the applications of Vernier Motor.
Ans.
- Direct Drive Appliations,
- High Torque at low Speed applications.
10. Define the following: (a) Detent torque, (b) Holding torque.
Ans.
Detent Torque: It is the maximum torque which the unenergised stepper Motor can withstand without slipping. It is also known as lagging torque.
Holding Torque: It is the maximum load torque which the energized stepper motor can withstand without slipping from equilibrium position.
11. What are the types of Power Controllers used for switched Reluctance motors?
Ans.
- Two power semiconductor devices and two diodes per phase.
- (n + 1) power switching devices and (n + 1) diodes.
- Phase winding with bifilar wires.
- C-dump circuit.
- Split-link circuit used with even phase number.
12. Write the advantages of Switched Reluctance motor.
Ans.
- No brushes, it requires less maintenance.
- It is a self starting machine.
- Due to less losses, it requires simple ventilation system.
- Absence of Rotor windings.
- It has No slip rings.
- Construction is very simple.
13. Give the expression for the emf and torque of a PMBLDC motor.
Ans.
Emf equation:
where,
- Bg – flux density in the air gap
- r – radius of the airgap
- l – length of the armature
- ωm – angular velocity in mech. rad/sec.
- Tph – number of turns/phase.
Torque equation:
where,
- Bg – flux density in the airgap
- r – radius of the air gap
- l – length of the armature
- I – current flow through the motor
- Tph – number of Turns/Phase.
14. Write the expressions for power input and torque of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor.
Ans.
Electromagnetic torque developed is given by,
15. What are the types of power controllers used for permanent magnet synchronous motor?
Ans.
- Fuzzy logic controller,
- PI controller.
16. What are the types of rotor available in synchronous reluctance motor?
Ans. Types of rotor in synchronous reluctance motor are
- Salient or segmental rotor,
- Radially laminated rotor,
- Axially laminated rotor.
17. Give the classification of stepper motor.
Ans.
Variable reluctance stepper motor:
- Single stack,
- Multi stack.
Permanent magnet stepper motor:
- Claw pole motor,
- Hybrid motors.
18. Define the term skewing.
Ans. Skewing or Slewing: Stopper motor operating at high speed is said to be slewing.
19. What is load commutation?
Ans. Load commutation is ensured only at high speeds. Whereas at low speeds the emf generated is not sufficient for load commutation.
20. What is the magnitude of stator current in PMSM to achieve demagnetization?
Ans. To achieve the demagnetization, the magnitude of stator current is sinusoidal distribution, and current rnagnitude as well as torque reduces.
21. State the Principle and operation of synchronous reluctance motor.
Ans. It is a single phase synchronous motor which does not require dc excitation to the rotor, known as synchronous reluctance motor,
Whenever a piece ferromagnetic material is located in a magnetic field, a force is exerted upon the material, tending to bring it into the position of the densest portion of the field. The force tends to align the specimen of material so that the reluctance of the magnetic path passing through the material will be at a minimum.
22. Write down the.expression for the electromagnetic torque of permanent magnet synchronous reluctance motor.
Ans.
where,
- L – is the inductance value per phase.
- I – is the current value per phase.
23. What are the types of Stepper motors?
Ans.
Without permanent magnet
- Variable reluctance motor.
With permanent magnet
- Claw pole motor,
- Hybrid motor.
24. List any four disadvantages of SRM.
Ans.
- No detent torque available when winding de-energies.
- Exhibit mid range resonance at some stepping rates.
- Normally available in 3.6° to 30° step angle.
- Low efficiency at low voltages and stepping rate.
25. Write down the torque equation of a switched reluctance motor drive.
Ans.
Where,
- L – is the inductance value per phase.
- I – is the current value per phase.
26. Draw the magnetic circuit of 2 pole permanent magnet brushless dc motor
Ans.
27. What are the applications of PMSM?
Ans.
- Power alternators,
- Textile and glass industries,
- Automotive applications,
- Computer and robotics applications.
28. What is meant self control?
Ans. It is a process of controlling the speed or current of the machine by the machine itself by using error and reference technique.
29. Write voltage and torque equations of a synchronous reluctance motor.
Ans. The torque of the reluctance machine can be given by
- Te – developed electrical torque,
- P – number of poles in the stator,
- δ – torque angle (or) load angle,
- Lds – direct axis inductance,
- Lqs – quadrature axis inductance.
30. Define reluctance torque.
Ans. The rate of change of energy transfer due to variation in stored energy or power due to variation in stored energy.
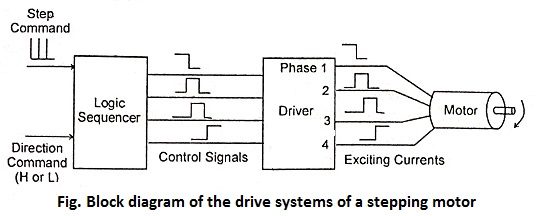
31. Draw the block diagram of the drive systems of a stepping motor.
Ans.
32. What is meant by hybrid stepping motor?
Ans. The hybrid motor is operated with the combined principles of the permanent and variable reluctance motor in order to achieve a small step angle and a high torque from a small size.
33. Explain why rotor position sensor is essential for the operations of SRM.
Ans. It is necessary to use a rotor position sensor for commutation and speed feedback. The turning ON and OFF operation of the various devices of power semiconductor switching circuit are influenced by signals obtained from rotor position sensor.
34. State the applications of switched reluctance motors.
Ans. Applications where the rotor must be held stationary for long periods and in potentially explosive environments such as mining because it does not have a mechanical commutator.
35. How are the directions of rotations reversed in case of PMBLDC motor?
Ans. The directions of rotations of PMBLDC motor can be reverse by changing the signals in the commutator and sensor arrangement.
36. What is electronic commutator?
Ans. The phase windings of PMBLDC motor is energized by using power semiconductor such as SCR, MOSFET, IGBT, power transistors, etc. switching circuits and sets as a commutator.
37. Write down the expressions for the self and synchronous reactance of permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Ans. Synchronous reactance is the sum of armature leakage reactance and fictitious reactance Xs = Xl + Xa.
38. List a few applications of PMSM.
Ans.
- Used as a direct drive traction motor.
- Used as high speed and high power drives for compressors, blowers, conveyors, fans, pumps, steel rolling mills, main line traction, ship propulsion and air craft facilities.
39. Give the operating principle of radial flux motor.
Ans. It has salient rotor shape such that the quadrature air gap is much larger than the direct air gap. This yields relatively small Ld/Lq ratio and results circulating flux in the rotor pole faces.
40. List the different modes of excitations in stepping motors.
Ans. The different modes of excitations are:
- mode I: One-phase on or full step operation.
- mode II: 2-phase on mode.
- mode III: Half step operation.
- mode IV: Micro stepping.
41. Write the voltage and torque equations of a switched reluctance motor.
Ans.
42. List the methods of rotor position sensing in switched reluctance motor.
Ans.
The rotor position sensing sensors and methods are
- Encoder position sensors,
- Half effect sensors,
- Search coils.
43. What is permeance co-efficient?
Ans. Also called the load-line, B/H or operating slope of a magnet. This is the line on the Demagnetization curve where a given magnet operates.
44. Name the power controller used in permanent magnet brushless DC motor.
Ans.
- Rotor position controller.
- Microcontroller (PIC).
- Speed controller.
- PWM control.
- Current control.
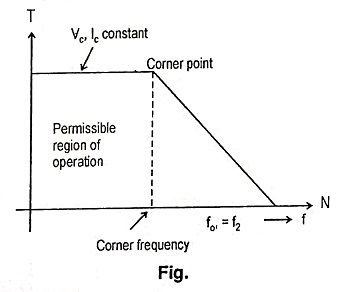
45. Draw the torque/speed characteristics of permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Ans.
46. Give some potential applications of synchronous reluctance machine.
Ans.
- Used as recording instruments, time devices, control apparatus, regulators and phonograph turntable.
- Proportioning devices on pumps or conveyors.
- Metering pumps.
- Synthetic fibre manufacturing equipment.
- Wrapping and folding machine.
47. Write the various design parameters of a synchronous reluctance motor.
Ans. The various design parameters are:
- Structure of the motor
- Rotor configuration
- Windings
48. Define torque constant of a stepper motor.
Ans. It is defined as the initial slope of the torque-current curve of the stepper motor. It is also called as torque sensitivity.
49. Why SR machines popular in adjustable speed drives?
Ans. Because of the presence of speed feedback control in the SR machine we can obtain adjustable speed. The speed feedback consists of a drive arrangement for angle variation so as to change the pulse angle and adjust the speed.
50. What is the significance of rotor position sensor is essential for the operation of SR motors?
Ans. It is necessary to use a rotor position sensor for commutation and speed feedback. The turning ON and OFF operation of the various devices of power semi conductor switching circuit are influenced by signals obtained from rotor position sensor.
51. Brief-up the advantages of load commutation in permanent magnet synchronous motors.
Ans.
- It runs at constant speed.
- No field winding, no field copper loss.
- Better efficiency.
- No sliding contacts, so it requires less maintenance.
52. What is meant by self-control?
Ans. Self control ensures that for all operating points the armature and rotor fields move exactly at the same speed.
53. List the types of synchronous reluctance motors.
Ans.
- Axially laminated.
- Radially laminated.
54. What is the function of drive circuit in stepping motor?
Ans. The output from the logic sequence generator signals are low level signals which are too weak to energize stepper motor windings. To increase the voltage, current and power levels of the logic sequence output by using power semiconductor switching This circuit is called power drive circuit
55. Define step angle in stepping motor.
Ans. It is the angular displacement of the rotor of a stepper motor for every pulse of excitation given to the stator windings of the motor.
56. Write the torque equation of switched reluctance motor?
Ans.
57. Mention some position sensors used in switched reluctance motor?
Ans. The position sensors are:
- Shaft position sensors.
- Optical encoders.
- Resolvers.
- Position sensors.
58. What is commutation?
Ans. The device which is used to measure the rotation of machine which is placed internally and based on it feedback is taken out.
59. Define synchronous reactance in PMSM.
Ans. It is the sum of armature leakage reactance and friction reactance Xs = Xl + Xa
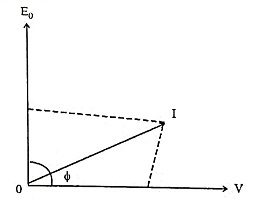
60. Draw the output phasor diagram of PMSM.
Ans.
61. What are the merits of 3-phase brushless permanent magnet synchronous motor?
Ans.
- The permanent magnet synchronous motor has higher efficiency due to the elimination of brushes, slip rings and field copper losses.
- It has superior power density.
- High torque to inertia ratio is its additional merit.
62. What are SYNREL motors?
Ans. The synchronous reluctance motor is said to be SYNREL Motor.
63. Write the factors of stepper motor which are responsible for its wide spread use?
Ans.
- When definite numbers of pulses are applied to the motor, the rotor rotates through definite known angle.
- Control of stepper motor is simple because neither a position or a speed sensor nor feedback loops are required for stepper motor to make the output response to follow the input command.
- Since the nature of command is in the form of pulses, stepping motors are compatible with modern digital equipment.
64. Define: Stepping angle.
Ans. Stepping angles is defined as the angle through which the stepper motor shaft rotates for each command pulse.
65. What is the significance of closed loop control in switched reluctance motor?
Ans.
- In hysteresis type current regulator, it maintains almost constant current over the entire speed range.
- Voltage PWM type current regulator, current is regulated using pulse width modulation and rotor feedback.
66. List out the advantages of switched reluctance motors.
Ans.
- Simple and robust construction with self starting.
- Since the rotor carries no windings, no brushes, the SRM requires less maintenance.
- The ventilation system for SRM is more easier as, more losses are taking place in the stator itself.
- The end turns are short and robust since the stator is simple to wind and there is no possibility of short-through fault.
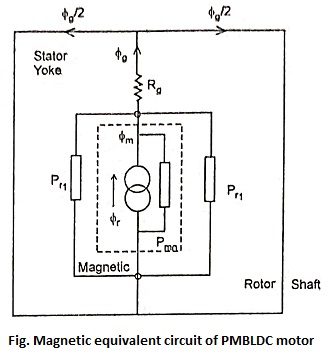
67. Draw the magnetic equivalent circuit of PMBLDC motor.
Ans.
68. Write torque and EMF equation of PM synchronous motor.
Ans.
Torque Equation:
Emf Eqquation:
69. Write significance of power controller of permanent magnet synchronous motors.
Ans.
- The control loop will be provided with inner current loop.
- Power controller have outer speed loop.
- Commutation will be at low speed.
- Four quadrant operation is possible.
70. Mention the different types of synchronous reluctance motor.
Ans.
Classification of synchronous reluctance motor according to rotor configuration.
- Cage rotor for line start.
- Cageless rotor for variable speed.
Classification according to the magnetization or lamination of the rotor.
- Radial type.
- Axial type.
71. Write the torque expression for synchronous reluctance motor.
Ans.
- Te – Development torque of synchronous reluctance motor.
- P – Number of poles.
- Ψ – The flux linkage induced by the field current.
- δ – Torque angle.
- Lds, Lgs – Direct and quadrature axis inductance with respect to syn rotating frame.
72. Write the principle of operation of stepping motors?
Ans. A stepper motor is a brushless DC motor whose rotor rotates in a discrete angular displacements when its stator windings are energized in a programmed manner. Rotation occurs because of magnetic interaction between rotor poles and poles of the sequentially energized stator winding. The rotor has no electrical windings but has salient or magnetized poles.
73. Give the advantages of sensorless operation of switched reluctance motor.
Ans.
- Since the rotor carries no windings, no brushes, the SRM requires less maintenance.
- Higher value of starting torque can be obtained without heavy in rush current.
74. Write the principle of operation of switched reluctance motor?
Ans. The switched reluctance motor develops an electromagnetic torque due to variable reluctance principle. When airgap is minimum, the reluctance will be minimum, hence inductance will be maximum, so the rate of change of inductance is zero.
When the reluctance varies, there will be a change in inductance so when a particular stator winding of SRM is excited, the rotor-pole comes in alignment with that stator pole and thus the rotor rotates.
75. What is meant by permeance co-efficient?
Ans. In the demagnetization characteristics, the line drawn from the origin through the operating point is called the load line and absolute value of its slope normalized to μ′0 is called the “permeance coefficient”.
76. List some permanent magnet materials.
Ans.
- Alnico
- Cobalt-Samarium
- Barium and strontium ferrites
- Neodynium – iron-boron.
77. Define synchronous reactance in permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Ans. The synchronous reactance is the fictitions reactance employed to account for the voltage effects in the armature circuit produced by the actual armature leakage reactance and the change in the airgap flux caused by armature reaction.
78. Give the applications of permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Ans.
- Low integral hp industrial drives.
- Fibre spinning mills.
- Used as high speed and high power drives for compressors, blowers, conveyors, fans, pumps, steel rolling mills and aircraft test facilities.