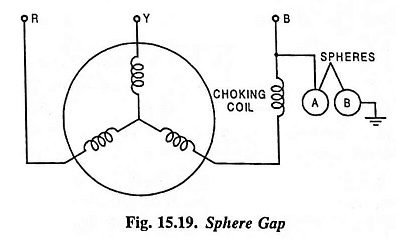
Sphere Gap Arrester Diagram:
In such a sphere gap arrester device the air gap is provided by two similar spheres—one connected to the line and another grounded. The spacing between the two spheres is very small compared with their diameter and can be adjusted with the help of gauge. A choking coil is inserted between the phase winding of the transformer and sphere connected to the line. This is done to reflect off any overvoltage surges that might tend to enter the transformer winding.
The minimum air gap is set so that a discharge does not take place at normal operating voltages but at predetermined excess voltages an arc is set up. This arc will travel up the spheres as the heated air near the arc tends to rise upwards. The arc will keep on travelling upwards and lengthening till it is interrupted automatically. When the source of voltages persists, a sound arc follows the first one and so on till the normal conditions of voltage are achieved.
Advantages:
It has the advantage of impulse ratio of unity, i.e., if the apparatus is protected against 50 cycle waves, it is protected against a wave of any duration.
Disadvantages:
Unfortunately, when the sphere gap arrester flashes over, the power current maintains the arc, which requires only a very low voltage to maintain it, and the arc is not self-extinguishing. The circuit breakers would have to intervene to interrupt the arc current and, therefore, the continuity of supply is interrupted. This is the reason that the sphere gap arrester is not of use.