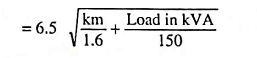Supply Systems Interview Questions and Answers:
1. What is the voltage that has been selected for HVDC transmission ?
Ans. ± 500 kV.
2. What is an electric power supply system ?
Ans. The system of generation, transmission and distribution of electrical power is called the electrical power supply system.
3. What is the usable voltage for secondary distribution ?
Ans. 415/240 V (415 volts for 3-phase loads and 240 V for single phase loads).
4. What is the difference between a feeder and distributor ?
Ans. Feeders are the conductors which connect the stations (in some cases generating stations) to the areas to be fed by those stations. Generally from feeders no tapping is taken to the consumers, therefore, current loading of a feeder remains the same along its length. It is designed mainly from the point of view of its current carrying capacity.
Distributors are the conductors from which numerous tappings for the supply to the consumers are taken. The current loading of a distributor varies along its length. Distributors are designed from the point of view of the voltage drop in them.
5. What is the legal requirement to which a distributor is subjected ?
Ans. A distributor is subject to the legal requirement that the voltage at the consumer’s terminals should be maintained within ±6% of the declared (or rated) voltage.
6. Why is ac distribution considered superior to dc ?
Ans. Distribution by ac system is undoubtedly superior to that by dc system as in ac system voltage control is easy by means of transformers.
7. List advantages of dc system over ac system.
Ans. DC system has the following advantages over dc system:
(i) Saving in conductor material, (ii) No inductance, capacitance, phase displacement and surge problem, (iii) No skin effect, (iv) Less insulation requirement, (v) No charging current, (vi) Less corona loss and reduced interference with communication circuits, (vii) Better voltage regulation, (viii) No stability problems and synchronizing difficulties.
8. Give limitations of ac transmission over dc transmission.
Ans. AC transmission has got the following limitations over dc transmission.
- In case of overhead lines spacing between the conductors is to be kept more in order to provide adequate insulation and to avoid corona loss.
- More copper is required.
- Greater the length of transmission line more is the capacitance of the line. There is a continuous loss on account of charging current even though the line is open.
- The construction of transmission lines for ac systems is not so easy as for dc systems.
- The alternators are to be synchronized before putting them into parallel.
- The variation in speeds of alternators are to be controlled within very low limits.
9. What is the percentage saving in feeder conductor if the line voltage in a 2-wire dc system be raised from 200 V to 500 V for the same power to be transmitted ?
Ans. 84%.
10. List various systems of transmission of electrical power.
Ans. Though in practice 3-phase 3-wire ac system is universally used for transmission and 3-phase 4-wire ac system is used for distribution of electric power but for special purposes other systems may also be used. The various systems of power transmission are :
(a) DC Systems :
- DC two-wire system.
- DC two-wire system with midpoint earthed.
- DC three-wire system.
(b) Single-Phase AC Systems:
- Single-phase two-wire system.
- Single-phase two-wire system with midpoint earthed.
- Single-phase three-wire system.
(c) Two-Phase AC Systems:
- Two-phase four-wire system.
- Two-phase three-wire system.
(d) Three-Phase AC Systems:
- Three-phase 3-wire system.
- Three-phase 4-wire system.
11. Why does the maximum voltage between each conductor and earth form the basis of comparison of volume of conductor material required in overhead system ?
Ans. In overhead system the conductors are insulated from the cross arms and supporting towers and as the towers and cross arms are earthed so the maximum voltage between each conductor and earth forms the basis of comparison of volume of conductor material required in overhead system.
12. Why does the maximum voltage between conductors form the basis of comparison of volume of conductor material required in underground system ?
Ans. In underground cables the maximum disruptive stress is between the two conductors of the cable; so the maximum voltage between conductors forms the basis of comparison of volume of conductor material required in underground system.
13. What is the ratio of volume of conductor material required for transmission of a given amount of power over a given distance by overhead system using (i) dc 2-wire system and (ii) 3-Φ, 3-wire ac system ?
Ans. 0.5/cos2Φ.
14. What is the ratio of volume of conductor material required for transmission of a given amount of power over a given distance by underground system using (i) Two-phase 4-wire system, (ii) Three-phase three-wire system.
Ans. Three-fourth.
15. What is the effect of voltage on transmission efficiency ?
Ans. The transmission efficiency increases with the increase in transmission voltage.
16. State the empirical formula for determining the system voltage of transmission line.
Ans. Approximate economical voltage for transmission in kV
17. What is modified version of kelvin’s law ?
Ans. According to Kelvin’s law the most economical cross section of a conductor is that which makes the annual cost of electrical energy wasted in the conductor equal to the annual cost of interest and depreciation on the capital cost of the conductor. This law was based on the assumption that the cost of the supporting structures e.g., towers, insulators and the cost of erection-cum-commissioning i.e., stringing of the conductors etc are fixed and independent of the area of cross section of the conductor. But this is not true in practice. So the Kelvin’s law was modified in order to take the above fact into account by assuming that the initial capital cost on the complete line installation can be split-up into two parts, one independent of the area of cross section of the conductor and the other dependent upon it, directly. Thus total annual fixed cost can be represented as Rs (P1 + P2a).