Testing of Materials Articles:
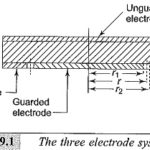
Direct Current Resistivity Method: The specimen shape and the electrode arrangement should be such that the Direct Current Resistivity Method can be easily calculated. For a solid specimen, the preferable shape is a flat plate with plane and parallel surfaces, usually … (Read More)
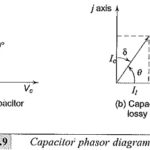
Dielectric Constant and Loss: Many insulating substances have dielectric constant greater than unity and have Dielectric Constant and Loss when subjected to a.c. voltages. These two quantities, namely, the dielectric constant and the loss depend on the magnitude of the voltage … (Read More)
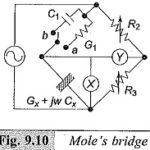
Mole Bridge for Low Frequency Measurements: The bridge that is usually used for low frequency measurements is the Mole Bridge whose schematic diagram is shown in Fig. 9.10. This is primarily devised to measure the dispersion in insulation of installed equipment … (Read More)
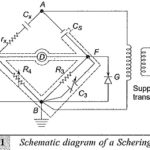
High Voltage Schering Bridge: In the power frequency range (25 to 100 Hz) High Voltage Schering Bridge is a very versatile and sensitive bridge and is readily suitable for high voltage measurements. The stress dependence of K′ or εr and tan δ … (Read More)
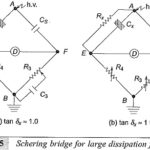
Dissipation Factor in Schering Bridge: Extension of range of the Dissipation Factor in Schering Bridge can be achieved by connecting in parallel an additional large capacitance across C3. But to avoid expensive and large-size decade capacitances the C3R3 arm is modified … (Read More)
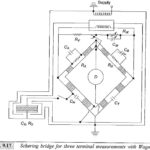
Schering Bridge Theory for Three Terminal Measurement: For two terminal measurements the bridge is grounded at its junction points. The supply transformer, detector, and all the components of the bridge are enclosed in earthed shields. For Schering Bridge Theory for Three … (Read More)
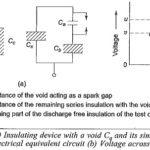
Partial Discharge Measurements: Earlier the testing of insulators and other equipment was based on the insulation resistance measurements, dissipation factor measurements and breakdown tests. It was observed that the dissipation factor (tan δ) was voltage dependent and hence became a criterion … (Read More)