Theory of PN Junction Diodes Articles:
Diode Failure Modes and Causes: We would certainly like for solid-state components to be 100% reliable but this is unfortunately not true. All solid-state devices have a certain probability of failure. To be good circuit designers and/or good circuit troubleshooters, we … (Read More)
Breakdown Voltage of PN Junction Diode: When an ordinary P-N junction diode is reverse biased, normally only very small reverse saturation current flows. This current is due to movement of minority carriers. It is almost independent of the voltage applied. However, … (Read More)
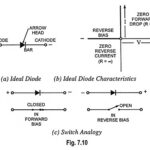
What is an Ideal Diode – Working and its V-I Characteristics: Diode is a two terminal device that permits only unidirectional conduction. It conducts well in the forward direction and poorly in the reverse direction. It would have been ideal if … (Read More)
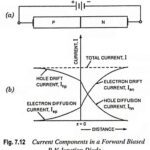
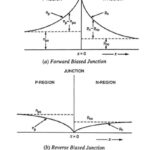
Current Components in PN Junction Diode: A Current Components in PN Junction Diode with a forward bias with an external voltage V is shown in Fig. 7.12 (a). Due to forward bias, there exists a potential gradient in P and N … (Read More)
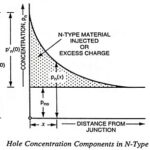
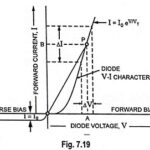
Quantitative Theory of PN Junction Diode: Here an expression for the total current will be derived as a function of the applied voltage with the assumption that depletion layer thickness is negligible (i.e., barrier … (Read More)
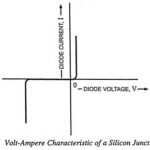
Terminal Characteristics of Junction Diodes: The volt-ampere characteristic of a silicon junction diode is depicted in Fig. 7.14. The same Terminal Characteristics of Junction Diodes is depicted in Fig. 7.15 with some scales expanded and others compressed to reveal details—the changes … (Read More)
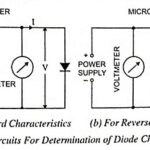
Determination of Diode Characteristics: The forward characteristics of a diode can be obtained by use of the circuit depicted in Fig. 7.16 (a). The diode voltage is set at a series of convenient levels, and the … (Read More)
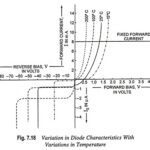
Effect of temperature on PN diode characteristics: Temperature on PN diode characteristics is very important consideration in the analysis or design of electronic devices or systems. It affects virtually all of the characteristics of a semiconductor device. The diode current at a … (Read More)
What is Diode Resistance? As already discussed, a forward-biased diode conducts easily whereas a reverse-biased diode restrains the flow of current, so a diode has a low forward resistance as compared to high blocking or reverse … (Read More)
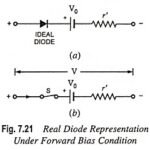
What is Real Diode? As already mentioned, an actual diode neither behaves as a perfect conductor when forward biased nor as a perfect insulator when reverse biased. When a diode is forward biased, it will not conduct till the potential barrier V0 … (Read More)
Up Down Circuit Analysis: Any circuit has independent variables (such as source voltages and branch resistances) and dependent variables (such as voltage drop across resistors, current and power). Determination of response of dependent variables to variation in independent variable is known … (Read More)
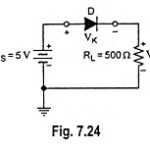
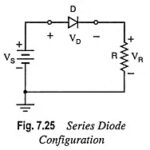
Series Diode Configurations with DC Inputs: The approximate models discussed in preceding section are used for investigation of a number of series diode configurations with dc inputs. This establishes a foundation in diode analysis that will carry over into the sections. … (Read More)
Diode as a Circuit Element: The P-N junction diode is considered as a circuit element. One of the most important application of diode is in rectification (i.e., in conversion of sinusoidal ac supply into dc … (Read More)
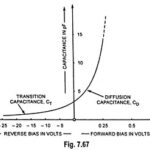
Transition and Diffusion Capacitance: Electronic devices are inherently sensitive to very high frequencies. Most shunt capacitive effects that can be ignored at lower frequencies due to very high reactance (XC being equal to 1/2πfC) cannot be ignored … (Read More)
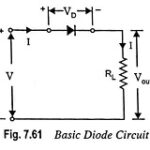
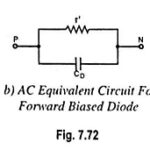
Equivalent Circuit of a Diode: It is usually advantageous to replace a device or system by its equivalent circuit. An equivalent circuit of a device or a system is a combination of electric elements properly chosen to best represent the actual … (Read More)
PN Diode Switching Times: A P-N junction diode may be used as an electrical switch. The electrical circuit can be made ‘on’ and ‘off’ by forward biasing or reverse biasing the diode. In both the cases, the diode response is accompanied … (Read More)
Switching Diode in Electronics: In discussing the rectifier diodes, the importance of reducing the reverse-bias current and the power losses under forward bias to the minimum was emphasized. But in case a junction diode is to be employed for high speed … (Read More)
PN Junction Diode Applications: An ideal PN Junction Diode Applications is a two terminal polarity sensitive device that has zero resistance (i.e., diode conducts) when it is forward biased and infinite resistance (i.e., diode does not conduct) when reverse biased. Because … (Read More)