Three Phase Synchronous Generator:
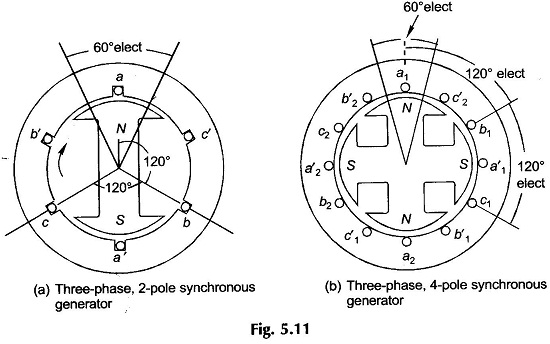
Practical synchronous generators are always of the 3-phase kind because of the well-known advantages of a 3-phase system. If two coils were located at two different space locations in the stator of Fig. 5.2, their emfs will have a time phase difference corresponding to their electrical space displacement. In Three Phase Synchronous Generator, if three coils are located in the stator of the 2-pole machine of Fig. 5.2 at relative electrical spacing of 120° (or 2π/3 rad), an elementary 3-phase machine results as is shown in Fig. 5.11(a).
The corresponding 4-pole arrangement is depicted in Fig. 5.11(b) where each phase has two symmetrically placed coils corresponding to each pair of poles.
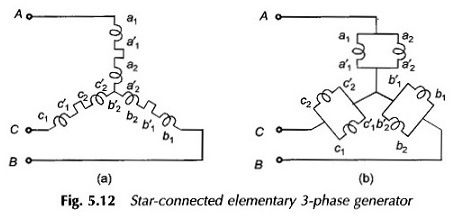
The coils of each phase are series/parallel connected and the three phases of a Synchronous generator are generally connected in star as shown in Figs 5.12(a) and (b).
The process of torque production in a machine will be explained already after gaining some familiarity with the rotating magnetic field produced by a current-carrying 3-phase winding.