Traction Drives Articles:
 Electric Traction Services: Electric Traction Services can be broadly classified as: Electric Trains. Electric buses, trams (or tramways) and trolleys. Battery driven and solar powered vehicles. Electric Trains: Electric trains run on fixed rails. They are further classified as Main Line Trains and Suburban Trains. Main Line … (Read More)
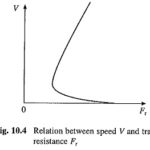
Electric Traction Services: Electric Traction Services can be broadly classified as: Electric Trains. Electric buses, trams (or tramways) and trolleys. Battery driven and solar powered vehicles. Electric Trains: Electric trains run on fixed rails. They are further classified as Main Line Trains and Suburban Trains. Main Line … (Read More)Nature of Traction Load: Nature of Traction Load describes as when the train runs at a constant velocity on level track, a number of frictional forces oppose its motion. The friction at bearings, guides etc. is classified as Internal Friction. The … (Read More)
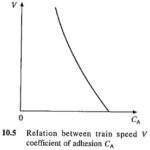
Coefficient of Adhesion in Traction: In Coefficient of Adhesion in Traction, the task of driving equipment consists of pushing the carriage on which it is mounted and pulling coaches and wagons behind it. Wheels coupled to the motors, either directly or … (Read More)
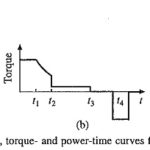
Duty Cycle of Traction Drives: The Duty Cycle of Traction Drives in trains is explained with the help of speed-, torque- and power-time diagrams (Fig. 10.6) which are drawn for travel between two consecutive stations on a levelled track. The train … (Read More)
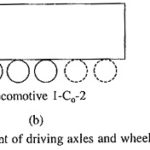
Driving Axle Code for Locomotives: Weight of the locomotive is supported on axles which are coupled to wheels. The weight per axle is limited by the strength of the track and bridges, and usually varies … (Read More)
Braking System in Train: Braking System in Train has number of advantages over mechanical braking. It reduces wear and tear on rails and wheels, substantially increasing their life. It is smooth, fast and can be precisely and automatically controlled. On the … (Read More)
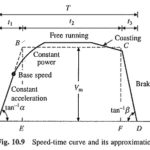
Traction Drive Rating and Energy Consumption: Traction Drive Rating and Energy Consumption – The speed-time curve of Fig. I0.6(a) is reproduced in Fig. 10.9. For simplification in calculations, it is approximated by a trapezoidal curve having constant values for acceleration and … (Read More)
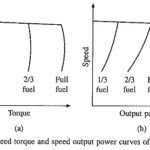
Features of Traction Drives: Various Features of Traction Drives are: 1. Large torque is required during start and acceleration in order to accelerate the heavy mass. 2. The motor is subjected to torque overloads during acceleration and when negotiating up gradients. 3. Because of … (Read More)
Traction Motors: Motors Employed in Traction : Earlier, dc series motor was widely used in Traction Motors. It has high starting torque and capability for high torque overloads. With an increase in torque, the flux also increases; therefore, for the same … (Read More)
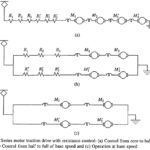
Conventional DC and AC Traction Drives: The commonly used Conventional DC and AC Traction Drives are The dc Traction Drives Employing Resistance Control: The dc traction drives employing resistance control are: 1500 V dc traction on Bombay-Igatpuri-Pune section for main line and Bombay suburban 750 … (Read More)
Semiconductor Converter Controlled Drives: These are now widely used both in ac and dc tractions involving dc and ac motors, and the conventional drives have all become outdated, and will be phased out in near future. The Semiconductor Converter Controlled Drives … (Read More)
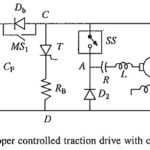
DC Traction using Semiconductor Chopper Controlled DC Motors: Chopper control has replaced resistance control in all dc traction schemes, such as 1500 V dc main line and suburban traction, 750 V dc underground traction and electric buses. The chopper control has … (Read More)
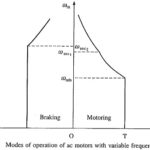
Polyphase AC Motors for Traction Drives: Advantages of ac motors over dc we already know. Because of negligible maintenance, ruggedness and higher power per unit weight or volume, the squirrel-cage induction motor is ideally … (Read More)
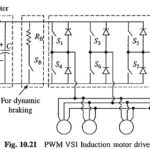
PWM VSI Induction Motor Drive: PWM VSI Induction Motor Drive for traction is shown in Fig. 10.21. A pulsewidth modulated voltage source inverter converts dc into variable frequency and variable voltage ac, which is then fed to induction motors. Each motor coach … (Read More)
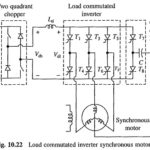
Load Commutated Inverter Fed Synchronous Motor Drive: Load Commutated Inverter Fed Synchronous Motor Drive is shown in Fig. 10.22. The inverter is a current source inverter employing thyristors T1 – T6. The commutation of inverter thyristor is done by the voltages induced in … (Read More)
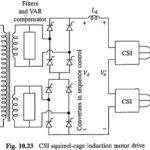
CSI Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Drive: Performance and operation of CSI induction motor drive is already explained . Figure 10.23 shows details of the traction drive of CSI Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Drive. In a multistage converter ac is converted into dc … (Read More)
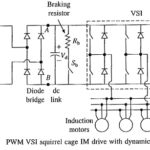
PWM VSI Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Drive: The PWM VSI Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Drive is shown in Fig. 10:24. dc link is supplied from ac source through a transformer and a diode rectifier. Because of the use of diode rectifier, … (Read More)
Diesel Electric Traction System: Because of high initial cost, electric traction is justified only where there is sufficient volume of traffic. Diesel Electric Traction System is preferable where the traffic is limited. Boundary between these two alternatives depends on several factors … (Read More)