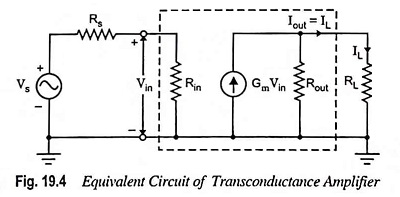
Transconductance Amplifier – Definition and Equivalent Circuit:
In transconductance amplifiers the input signal is a voltage and its output signal is a current. The ideal transconductance amplifier provides an output current which is proportional to the signal voltage and the proportionality constant is independent of the magnitudes of Rs and RL.
From the equivalent circuit of a transconductance amplifier depicted in Fig. 19.4, we find that if Rs << Rin, then Vin ≈ Vs and if load resistance RL << Rout,
then
and
An ideal transconductance amplifier should have infinite input and output resistances.