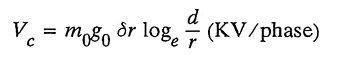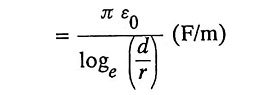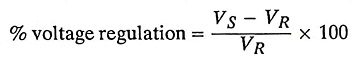Transmission and Distribution Interview Questions and Answers:
Following are the below Transmission and Distribution Interview Questions and Answers, Transmission and Distribution Important Questions and Answers
1. List out the advantages of high voltage A.C. transmission.
Ans. Advantages of HVAC are
- The maintenance of ac substations is easy and cheaper.
- The ac voltage can be stepped up or stepped down by transformers with ease and efficiency. This permits to transmit power at high voltages.
- The line losses are less.
2. What is meant by stringing chart?
Ans. Stringing Chart: It is a chart, very useful:
- In the field work for stringing the conductors.
- For adjusting the conductors to proper sag and tension.
- For obtaining the values of sag and tension at any temperature.
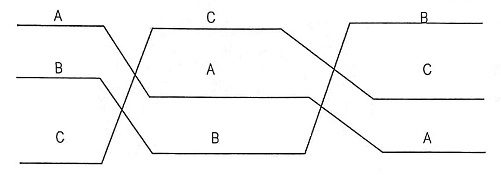
3. What is the need of transposition?
Ans. Need of Transposition:
- The effect of transposition is that each conductor has the same average inductance.
- After transposition, the voltage drops are equal in all conductors.
4. Define the term critical disruptive voltage.
Ans. Critical Disruptive Voltage:
It is the minimum phase-neutral voltage at which corona occurs
where
- m0 = 0.8 to 0.87 for stranded conductors
- g0 = breakdown strength of air at 76 cm of mercury
- δ = air density factor
- γ = radius of conductor (m)
- d = spacing between conductors (m).
5. Distinguish between attenuation and phase constant.
Ans.
| Sl no | Attenuation Constant | Phase Constant |
| 1 | It is the real component of propagation constant of a line. | It is the imaginary component of propagation constant of a line. |
| 2 | Its unit is Neper/metre. | Its unit is radians/metre. |
6. What is meant by Ferranti effect?
Ans. In long transmission lines and cables recovering end voltage is greater than sending end voltage during light load conditions or no load operation. Under these conditions capacitance associated with the line generate more reactive power that the reactive power which is absorbed. Hence VR > VS. This effect is known as Ferranti effect.
7. What are the advantages of string insulator?
Ans. Advantages of String Insulators:
- For higher voltages, these are cheaper than pin insulator.
- Each unit is designed for low voltage level such as 11 kV but by connecting such units in series to form a string, insulator for any higher voltage level can be designed.
- The string is suspended and is free to swing in any direction. So it takes the position so that mechanical stresses on the line are minimum.
- This type of insulators provides greater flexibility to the line.
8. What are the various methods of earthing in substations?
Ans. Methods of Earthing in Sub-Stations:
- Pipe Earthing
- Plate Earthing
- Rod Earthing
- Wire (Strip) Earthing
- Earthing through a water mains.
9. Define the terms feeders and service mains.
Ans.
Feeders: Feeders are conductors which help in transfer of power from receiving station to the substation.
Service Mains: In crowded areas, overhead system of bare conductors is not practicable. In such cases insulated conductors are used in the form of underground cables to give supply to consumers. These cables are called service mains.
10. List out the objectives of FACTs?
Ans.
- Rapid control of reactive power flow and voltage profile using series and shunt connected controllers.
- Secure loading of lines close to their thermal units.
- Improve power transferability, transient stability and dynamic stability during fault switching etc.
11. What are the advantages of using bundled conductors?
Ans.
- Reduced reactance due to increase in self GMD.
- Reduced voltage surface gradient.
- Reduced corona loss.
- Reduced radio interference.
- Reduced surge impedance.
- Reduced inductance.
- Increases the power capability of the line.
- Increases surge impedance loading.
12. What are the factors which affect corona?
Ans. The factors affecting the corona are:
(a) Atmospheric Factors
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Dust and Dirt
- Rain, Snow and Fog.
(b) Electrical factors
- Frequency
- Supply voltage.
(c) Effect of line conditions
- Conductor spacing
- Diameter of conductor
- Shape of conductor
- Surface condition
- Number of conductors per phase
- Heating of conductor by load current.
13. What is the use of power circle diagram?
Ans. The use of power circle is to determine the maximum power that can be transmitted over the line both at the receiving end and sending end.
14. Enumerate the different types of insulators used for overhead transmission lines.
Ans.
The types of insulators used for overhead transmission line:
- Pin type insulator
- Suspension type insulator
- Strain insulator
- Shackle insulator
- Stay insulators.
15. How are cables classified based on an operating voltage?
Ans.
- Low voltage or L.T upto 1000 V
- High voltage or H.T upto 11 kV
- Super Tension (S.T) upto 33 kV
- Extra High Voltage upto 132 kV
- Extra Super Power Cables — Above 132 kV.
16. What are the bus bar components?
Ans. The components of the bus bar are transformers, circuit breakers, isolators, current transformers, potential transformers, protective relays, lightening arrestors, control room equipments.
17. What are the advantages of neutral grounding?
Ans. The advantages of neutral grounding are:
- Line to neutral (i.e) Phase voltage are limited to phase to ground voltage during any fault.
- The arcing occurs between neutral and ground when there is high voltage or transient due to line to ground fault. This arcing ground is eliminated by neutral grounding.
- Protective relays which are more sensitive against line to ground faults can be incorporated in the system.
- The over voltages due to lighting and switching surges are discharged to the ground. If not these high voltage waves get reflected at the isolated neutral of the system and increases line voltage.
18. Give any two factors that affect sag in an overhead line.
Ans.
- Wind Pressure
- Ice loading.
19. Write the expression for a capacitance of a 1Φ Transmission line.
Ans. Capacitance of a transmission line.
where
- ε0 = 8.854 x 10-12 (F/m),
- d = distance of separation between two conductors(m),
- r = radius of each conductor(m).
20. What is skin effect?
Ans. An alternating current passing through a conductor tends to distribute itself non-uniformly throughout the cross section. The portions of conductor situated at or near the surface carry a major portion of total current. This is known as skin effect.
21. Define voltage regulation in connection with transmission lines.
Ans. When current flows through a transmission line, there is a voltage drop in the line due to resistance and inductance of line. This causes the receiving end voltage (VR) to reduce below the sending end voltage (VS). The difference in voltage at receiving end of a transmission line between conditions of no load and full load is called as voltage regulation.
22. What is the range of surge impedance in case of underground cables?
Ans. Surge impedance of underground cable = 40 to 50 Ω.
23. Define grading of cables.
Ans. Grading of cables is defined as “the process of achieving uniform electrostatic stress in the dielectric of cables”. The two types of grading are:
- Intersheath grading,
- Capacitance grading.
24. What is meant by birdage?
Ans. Short-circuiting of the line conductor to earth through the large birds or similar objects is known as Birdage.
25. What is ring main distributor?
Ans. Ring main distributor is a distributor starts from one point, makes a loop through the area to be served and returns to original point. It can be fed at one or more points.
26. List the types of substations.
Ans.
Classification according to Service
- Transformer substations
- Switching substations
- Power factor correction substations
- Converting substations
- Industrial substations
Classification according to Construction
- Indoor substation
- Outdoor substation
- Underground substation
- Pole mounted substation
27. List the types of HVDC links.
Ans.
- Monopolar link
- Homopolar link
- Bipolar link.
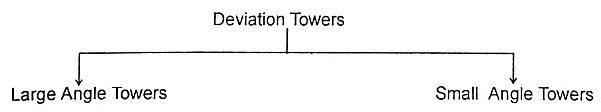
28. What is deviation tower?
Ans. Deviation towers are used with strain insulators. They are used at points where transmission line changes direction. These towers are designed to withstand the resultant forces due to change in direction.
29. What is proximity effect?
Ans. The inductance and the current distribution in a conductor is affected by the presence of other conductors in its vicinity. This affect is known as proximity effect.
30. Define visual critical voltage.
Ans. Visual critical voltage is the minimum phase-neutral voltage at which corona glow appears all along the line conductors.
31. What is the range of surge impedance for an OH Transmission line?
Ans.
Surge Impedance for an OH Transmission Line
= (0.4 to 0.6) kΩ.
32. Mention any 4 insulating materials for cables.
Ans.
- Rubber
- PVC
- Butyl rubber
- Oil impregnated paper
- Polyethylene thermoplastic.
33. What are the methods of improving string efficiency?
Ans.
- By grading the insulators
- By using a guard ring
- By using longer cross-arms.
34. What is a distributor?
Ans. Distributors are conductors where tappings are taken to transfer power to the consumers. A distributor line supplies consumers directly at short intervals along the line.
35. Mention any 4 bus schemes in the substation.
Ans.
- Mesh scheme,
- Main and transfer bus-bar scheme,
- Single bus scheme,
- Double bus-bar scheme.