Different Types of Relays Elements:
The Important Different Types of Relays Elements or also called Electromagnetic Types are
- Induction Disc Relay
- Induction-cup Relays
- Moving Coil Relays
- Hinged Armature Relays
- Polarized Moving Iron Relays
- Moving Iron and Balanced Beam Relays
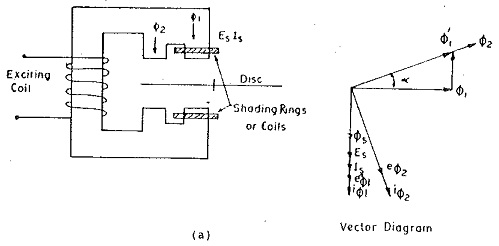
1.Induction Disc Relay:
The shaded pole type gives the most effective form of an electromagnet since it has the following:
- Higher torque/VA.
- A single coil which permits use of larger wire.
- Time-current characteristics which can be controlled easily by varying the number of laminations in the coil and the impedance of the shading Boil circuit, or by magnetic shunts.
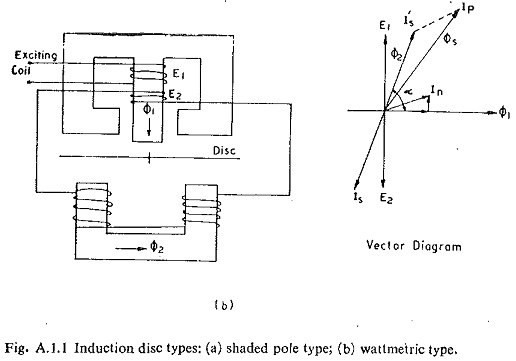
The wattmetric type is now becoming obsolete since it has more windings, less overload capacity and less torque/VA.
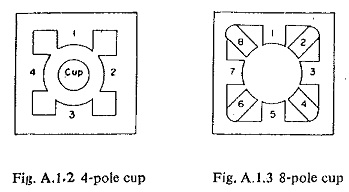
2.Induction-cup Relays:
For high speed operation where polarizing and/or differential windings are required, a 4-pole electromagnet is used. No damping is required, and the disc is formed into a cup to minimize inertia-. Any Types of Relay characteristic could be obtained just by changing the coil windings. If saturation is avoided, operating characteristics can be linear and accurate; pick-up and reset values are close together.
Advantages of Induction-cup Relays:
- These are ideal as directional relays because of their high sensitivity and speed and because the parasitic torque due to current and potential alone can be made small and can be adjusted out by a vane on the cup and a flat cut on the rotatable centre core,
- The rotor (cup) has no connecting leads and can be removed quickly without disturbing contact settings.
- Variations like the 8-pole and 6-pole units can be made.
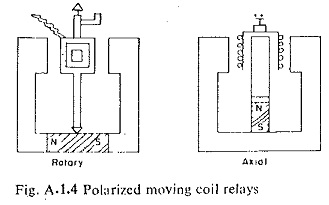
3.Moving Coil Relays:
Another Different Types of Relays Elements is Moving Coil Relays. It Consists of two types:
- Rotary- moving coil.
- Axially moving coil.
The rotary type is cheaper and uses standard jewel bearings and d.c. instrument construction.
The axial type has twice the sensitivity because of the single radial magnetic gap. Typical sensitivity is 1/2 mW for just closing the contacts.
Higher speeds are obtained with aluminium former while slower speed and heavier damping are obtained with copper formers.
4.Hinged Armature Relays:
These are used mainly as auxiliary relays, e.g tripping relays, a.c. and d.c. voltage and current relays.
Their VA consumption is low being of the order of 0.05 W at pick-up with one contact. The VA consumption will increase with the number of contacts. They can be polarized for sensitive d.c. operation by the addition of a permanent magnet.
5.Polarized Moving Iron Relays:
Their sensitivity can approach that of the moving coil Types of Relay and they have a more robust construction. Most of them use leaf-spring supported armature.
6.Moving Iron and Balanced Beam Relays:
In these Different Types of Relays Elements have a low ratio of reset/operating current.
If set for fast operation, there is tendency to overreach on transient conditions. There are large second harmonic torques developed. The pull of each magnet is proportional to the square of the current in its coil. Mechanical bias may be provided by gravity or by a spring.