Underground Cables in Power System Articles:
Underground Cables: Electric power can be transmitted or distributed either by overhead system or by underground cables. The underground cables have several advantages such as less liable to damage through storms or lightning, low maintenance cost, less chances of faults, smaller voltage … (Read More)
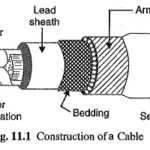
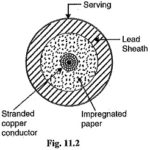
Construction of Underground Cables: Fig. 11.1 shows the general Construction of Underground Cables. The various parts are : Cores or Conductors: A cable may have one or more than one core (conductor) depending upon the type of service for which it is intended. … (Read More)
Insulating Materials for Underground Cables: The satisfactory operation of a cable depends to a great extent upon the characteristics of insulation used. Therefore, the proper choice of Insulating Materials for Underground Cables is of considerable importance. In general, the insulating materials … (Read More)
Classification of Underground Cables: Classification of Underground Cables may be in two ways according to the type of insulating material used in their manufacture the voltage for which they are manufactured. However, the latter method of Classification of Underground Cables is generally … (Read More)
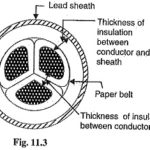
Three Phase Service Cable: In practice, underground cables are generally required to deliver 3-phase power. For the purpose, either three-core cable or three single core cables may be used. For voltages upto 66 kV, 3-core cable multi-core construction) is preferred due … (Read More)
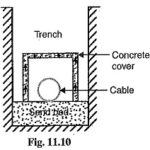
Laying of Underground Cables: The reliability of Laying of Underground Cables network depends to a considerable extent upon the proper laying and attachment of fittings i.e., cable end boxes, joints, branch connectors etc. There are three main methods of Laying of Underground … (Read More)
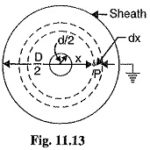
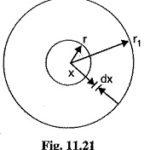
Capacitance of Single Core Cable: A Capacitance of Single Core Cable can be considered to be equivalent to two long co-axial cylinders. The conductor (or core) of the cable is the inner cylinder while the outer cylinder is represented by lead … (Read More)
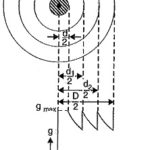
Grading of Cables: The process of achieving uniform electrostatic stress in the dielectric of cables is known as grading of cables. It has already been shown that electrostatic stress in a single core cable has a maximum value (gmax) at the conductor … (Read More)
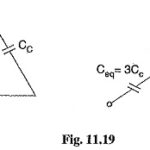
Capacitance of 3 Core Cables: The Capacitance of 3 Core Cables is much more important than that of overhead line because in cables (i) conductors are nearer to each other and to the earthed sheath (ii) they are separated by a dielectric … (Read More)
Thermal Resistance to Heat Flow: The Thermal Resistance to Heat Flow between two points in a medium (e.g. insulation) is equal to temperature difference between these points divided by the heat flowing between them in a unit time i e. In SI … (Read More)
Types of Cable Faults: Cables are generally laid directly in the ground or in ducts in the underground distribution system. For this reason, there are little chances of faults in underground cables. However, if a fault does occur, it is difficult … (Read More)
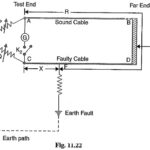
Loop Tests in Underground Cables: There are several methods for locating the faults in underground cables. However, two popular methods known as Loop Tests in Underground Cables are : Murray loop test Varley loop test These simple tests can be used to locate the … (Read More)