What is Alphanumeric Codes? – ASCII code, EBCDIC Code:
In order to communicate, we need not only numbers but also letters of alphabet, punctuation marks and other special characters. These codes are called alphanumeric codes. Most of these codes, however, also represent symbols and various instructions necessary for conveying intelligible information.
Different codes are used for representing alphanumeric data stored in paper tape, punched card or magnetic tape for use by a line printer or typewriter. The most common alphanumeric codes are ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange and EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code).
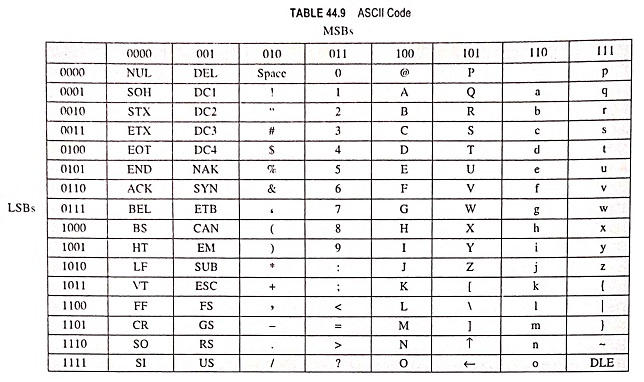
ASCII, pronounced “askee” is perhaps the most widely used alphanumeric code. It is a seven-bit code in which the decimal digits are represented by the 8-4-2-1 BCD code preceded by 011. It has 27 i.e., 128 possible code groups which is more than enough to represent all of the standard keyboard characters as well as control functions such as the (RETURN) and (LINEFEED). This code is used for the transfer of alphanumeric information between a computer and input/output devices such as video terminals or printers. A computer also uses it internally to store the information that an operator types in at the computer’s keyboard.
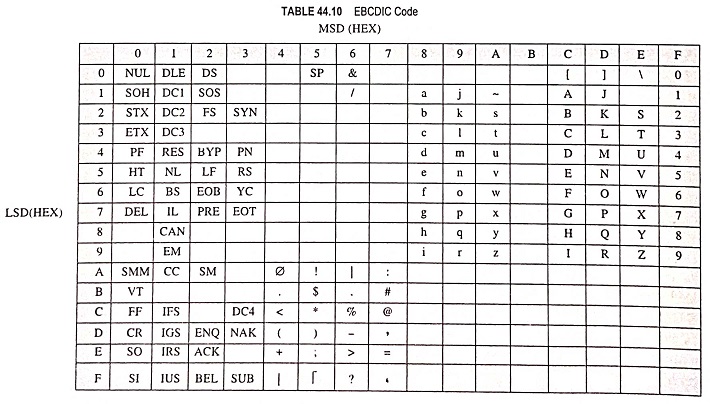
EBCDIC is an eight-bit code in which the decimal digits are represented by the 8421 BCD code preceded by 111.
Table 44.9 shows the ASCII code groups. For each of presentation they are listed with the three most significant bits (MSBs) of each group along the top row and the four least significant bits (LSBs) along the left column. For instance, the letter A is represented by 1000001, the comma by 0101100 and DEL by 0010000.
EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code) pronounced as ‘eb-si-dik’ is an eight-bit code in which the decimal digits are represented by the 8421 BCD code preceded by 1111. Both lower case and upper case letters are represented in addition to numerous other symbols and commands. It is used by most large computers to communicate in alphanumeric data. Table 44.10 shows the EBDIC code. For example, upper case letter A is represented by C1.