What is Bleeder Resistor? – Working and Its Functions
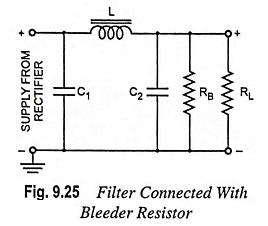
The operation of an inductor filter is based on the fact that a minimum current flows through it at all times. To provide flow of this minimum current at all times through the choke, a resistor called the bleeder resistor is placed across the filter output, as illustrated in Fig. 9.25. Thus it is used to maintain a certain minimum current through the choke, even the load resistor gets open circuited, and improves the filtering action. The value of bleeder resistance should be such as to draw only 10% of total load current.
The bleeder resistors can serve a number of functions as given below :
1. It improves the voltage regulation. Being connected permanently across the supply it causes an initial voltage drop and on connecting the load there is a slightly additional voltage drop. Thus the difference between the no-load voltage and full-load voltage is reduced thereby improving the regulation.
2. It provides the safety to the operator by providing a discharge path to the capacitor. When power supply is switched off, the filter capacitor discharges through it. That is why it is called the bleeder resistor. If bleeder resistor is not connected across the filter output, the capacitor will retain its charge for quite sometime even when the power supply is switched off and this high voltage can be dangerous to the operational staff. Thus the hazard of electrical shock is reduced.
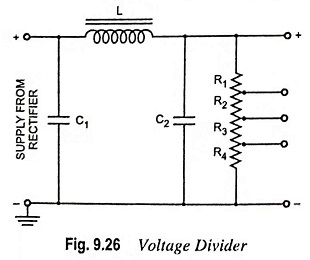
3. A single power supply may be required to provide more than one voltage for the operation of electronic devices/circuits. Bleeder resistor can be used as a voltage divider for tapping out any desired output voltage, as shown in Fig. 9.26. In this case the bleeder resistor may consist of two to four resistors connected in series, as shown in the Fig. 9.26.