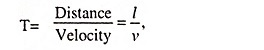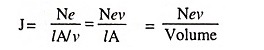What is Current Density?
By definition, the current density, denoted by the symbol J, is the current per unit area of the conducting medium i.e.,
where
- current I is the rate of flow of charge.
If N is the free electron density moving in the conducting medium, e is the charge of electron, then the rate of flow of charge is given by
Thus the current density J is given by
But the time
Therefore,
Current density,
where
- lA is the volume of conductor
where
- ρ = ne, the charge density, in coulombs per cubic metre and
- ν = is the velocity in metres per second.
The above derivation is independent of the form of conducting medium. Consequently, it is not necessary that the conducting medium is a wire conductor. It may be equally well a portion of gaseous-discharge tube or a volume element in the space-charge cloud of a vacuum tube or semiconductor. Furthermore, neither ρ nor ν need be constant, but may vary from point to point in space or may vary with time.