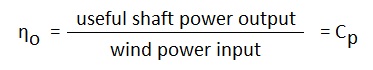Wind Energy and Wind Power Plant:
Wind is a form of solar energy. It is caused by the uneven heating of the atmosphere by the sun due to the irregularities of the earth’s surface, and rotation of the earth. Wind flow patterns are modified by the earth’s terrain, bodies of water, and vegetative cover. The terms “wind energy” or “wind power” describe the process by which the wind is used to generate mechanical power or electricity. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical power. This flow, or kinetic energy of the wind, can be “harvested” with the help of modern wind turbines, and can be used for various applications including generation of electricity by coupling the turbine to a generator. This mechanical power can be used for specific tasks like grinding grain, saw milling, pumping water or electricity to power homes, businesses, schools, etc.
Advantages of Wind energy:
- Wind energy is a free.
- Renewable resource.
- Wind energy is also a source of clean, non-polluting, electricity.
- Low operation cost.
- Wind turbines can be located on land that is also used for grazing or even farming.
Disadvantages of Wind energy:
- A higher initial investment.
- Cost of the machinery is high.
- Environmental concerns.
- The noise produced by the rotor blades.
- Birds and bats having been killed (avian/bat mortality) by flying into the rotors.
- Good wind sites are often located in remote locations far from load centre.
Characteristic of a good wind power plant site:
- High annual wind speed.
- A mountain gap.
- An open plain or an open shore line.
- There should not be any obstruction within a radius of 3 km.
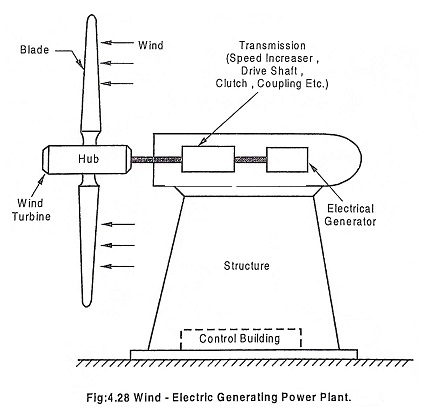
Wind-Electrical generating power plant:
The various components of a wind electric generating power plant are:
1. Wind Turbines or rotor
Wind turbines, like aircraft propeller blades, get turned by the moving air and power an electric generator that supplies an electric current. Simply stated, a wind turbine is the opposite of a fan. Instead of using electricity to circulate wind in a fan, wind turbines use wind to make electricity. The wind turns the blades, which spin a shaft, which connects to a generator and makes electricity.
2. Wind mill head
The wind mill supports the rotor housing and bearing, it also houses control mechanism like changing blades pitch for safety device and allow the rotor to face the wind.
3. Electrical generator
It is coupled to the turbine and generates electricity.
4. Supporting structure
It is designed to withstand the wind force and the self load of the plant.
Wind Turbine Types:
Modern wind turbines fall into two basic groups;
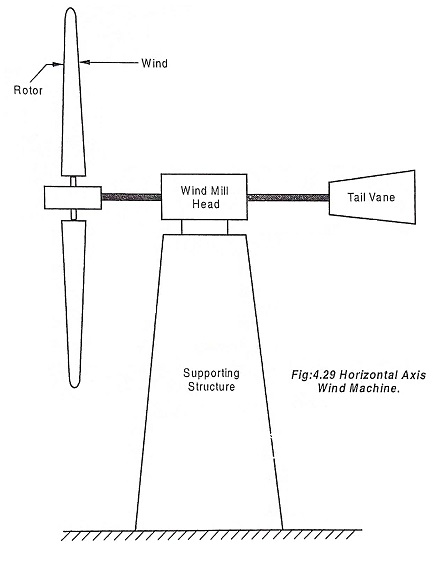
- The horizontal-axis variety, like the traditional farm windmills used for pumping water, and
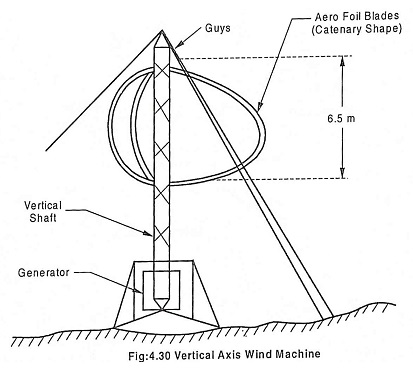
- The vertical-axis design, like the eggbeater-style Darrieus model, named after its French inventor. Most large modern wind turbines are horizontal-axis turbines.
Horizontal turbine components include:
- Blade or rotor, which converts the energy in the wind to rotational shaft energy.
- A drive train, usually includes a gearbox and a generator.
- Horizontal shaft that transfer energy from mills to rotor.
- A tower that supports the rotor and drive train; and
- Other equipments, including controls, electrical cables, ground support equipment, and interconnection equipment.
Vertical turbine components include:
- Aerofoil blades or rotor, which converts the energy in the wind to rotational shaft energy;
- Guys that supports the shaft and generator;
- Vertical shaft that transfer energy from mills to rotor;
- Generator that produces electricity;
- Other equipments, including controls, electrical cables, ground support equipment, and interconnection equipment.
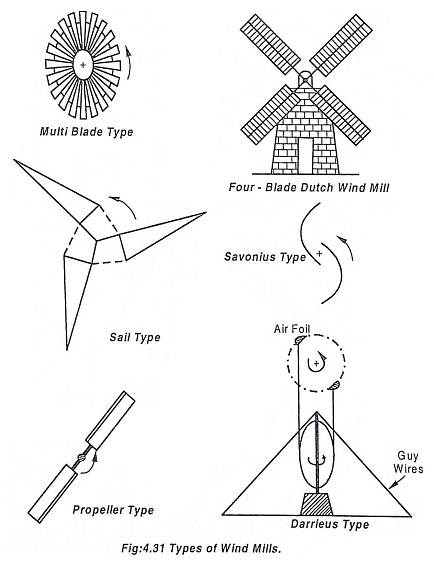
Types of wind mills:
Wind mill comes in various shape and size and can be categorised into different types as shown in Fig.4.31.
- Multiple blade type
- Propeller type
- Sail type
- Darrieus type
- Savonius type
The multiple blade type is the widely used wind mill, it may have 10 to 20 numbers of blades made up of metal sheets.
The propeller type of mill has two blades which is connected through a rod and the centre of the rod is mounted over the hub.
The sail type has three blades made up of triangular pieces cloths that are stitched out together.
All the above three blades has low rotating speed upto 80 r.p.m.
Darrieus type wind mill needs much less surface area, it looks like an egg heater and may have two or three aerofoil blades, It is best suited for vertical wind power plant, it has high speed, high efficiency and low cost but it is not self starting.
Savonious type wind mill consists of hollow cylinder sliced into two half and are mounted over vertical shaft with a gap in between. Due to the gap between the two half tongue is produced. It needs a large surface area. It is self starting but has low speed and low efficiency.
Performance of wind machine:
The wind electrical plant should properly utilize the wind energy in the best possible method. The overall efficiency of the plant is calculated by
ηo = ηA · ηg · ηc ·ηgen
where
- ηo = overall efficiency of the power plant
- ηA = efficiency of the aeroturbine
- ηg = efficiency of the Gearing
- ηc = efficiency of the coupling
- ηGen = efficiency of the Generator
Therefore
where
- Cp = Co-efficient of performance
- Cp of an horizontal axis wind machine is 0.593
Wind speed plays a very important role in the power output as the efficiency of the system depends on design of wind rotor and speed of rotation of blade.
Speed of rotation of blade = VT/V
where
- VT = Blade speed
- V = Wind speed
Blade speed VT = πDN m/sec
where
- D = Diameter of rotor
- N = Rotation frequency or rotation per second